The Medical waste disposal regulations can often seem complex and daunting, particularly for healthcare facilities that generate significant amounts of potentially hazardous waste. These regulations are crucial for ensuring that medical waste, which can include everything from contaminated sharps to pathological specimens, is managed in a way that protects public health and the environment. This article aims to demystify medical waste disposal regulations by outlining key compliance strategies that healthcare facilities should follow to meet these essential requirements.
Introduction to Medical Waste Disposal Regulations
Medical waste disposal regulations are designed to govern how waste produced by healthcare settings is handled, treated, and disposed of. These regulations help minimize the risks associated with medical waste, which can be infectious, toxic, or otherwise harmful. Compliance with these regulations is not only a legal obligation but also a critical aspect of maintaining safety and environmental stewardship.
Understanding these regulations involves knowing the types of waste that fall under their purview, the procedures for handling and treating this waste, and the specific requirements for disposal. By adhering to these regulations, healthcare facilities can ensure they are protecting their staff, patients, and the environment from the risks posed by medical waste.
Key Compliance Strategies for Medical Waste Disposal Regulations
Accurate Waste Classification and Segregation
Proper classification and segregation of medical waste are foundational to compliance with medical waste disposal regulations. The correct handling and disposal methods depend on accurately identifying the type of waste generated. Key steps include:
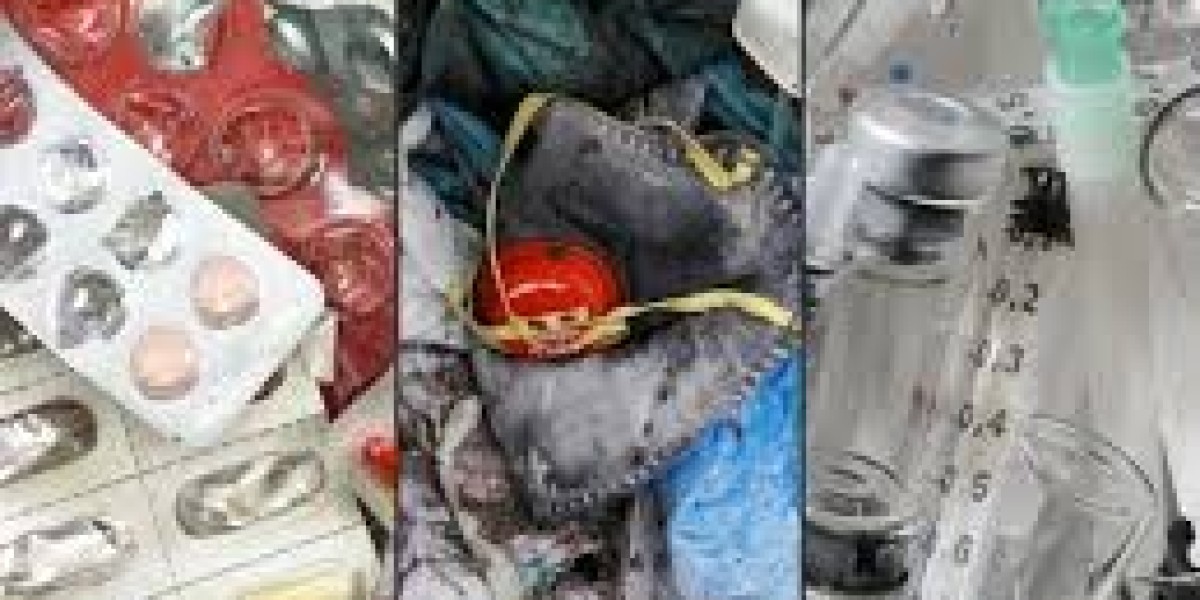
- Categorization: Waste should be classified into categories such as infectious waste, hazardous waste, and sharps. For example, infectious waste might include used bandages and contaminated gloves, while sharps include needles and scalpel blades.
- Color-Coding and Labeling: Use color-coded containers and clear labels to distinguish between different types of waste. This helps in ensuring that waste is handled and disposed of correctly according to its classification.
By accurately classifying and segregating medical waste, facilities can ensure that it is managed according to the appropriate standards, thus meeting regulatory requirements.
Safe Handling and Storage Procedures
The safe handling and storage of medical waste are critical to minimizing risks and complying with medical waste disposal regulations. Effective practices include:
- Containment: Use suitable containers for different types of medical waste. For instance, sharps should be placed in puncture-resistant containers, while infectious waste should be stored in leak-proof bags.
- Storage Conditions: Designate specific areas for storing medical waste. These areas should be secure, well-ventilated, and equipped with secondary containment systems to manage spills and leaks.
Following these handling and storage procedures helps prevent accidental exposure and contamination, thus ensuring compliance with medical waste disposal regulations.
Treatment and Disposal Methods
Treatment and disposal methods for medical waste are regulated to ensure that waste is processed in a way that mitigates health and environmental risks. Key methods include:
- Autoclaving: This method uses high-pressure steam to sterilize medical waste, particularly effective for waste that is predominantly biological in nature. Autoclaving is widely used in healthcare settings to treat waste before disposal.
- Incineration: Incineration involves burning waste at high temperatures to reduce its volume and neutralize harmful substances. This method is suitable for waste that cannot be treated by other means, such as pathological waste.
- Chemical Disinfection: Chemical treatment involves using chemicals to neutralize hazardous components. This method is used for certain types of waste, such as those contaminated with chemicals or pharmaceuticals.
Compliance with treatment protocols ensures that medical waste is managed in a manner that meets regulatory standards and minimizes risks.
Best Practices for Ongoing Compliance
To maintain ongoing compliance with medical waste disposal regulations, healthcare facilities should adopt the following best practices:
Regular Staff Training: Provide comprehensive and regular training for staff involved in waste management. Training should cover the latest regulations, handling procedures, and emergency response protocols.
Routine Audits and Inspections: Conduct regular audits and inspections to assess compliance with medical waste disposal regulations. This helps identify any potential issues and ensures that procedures are consistently followed.
Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintain detailed records of waste generation, handling, treatment, and disposal activities. Proper documentation is essential for demonstrating compliance and managing waste effectively.
Stay Updated on Regulatory Changes: Keep informed about updates to medical waste disposal regulations. Regulations may evolve over time, and staying current ensures that your facility continues to meet all requirements.
Understanding and adhering to medical waste disposal regulations is essential for ensuring that medical waste is managed safely and effectively. By accurately classifying and segregating waste, following safe handling and storage procedures, and implementing appropriate treatment and disposal methods, healthcare facilities can achieve compliance and protect public health and the environment. Adopting best practices for ongoing compliance further supports effective waste management and contributes to a safer, more sustainable healthcare environment.