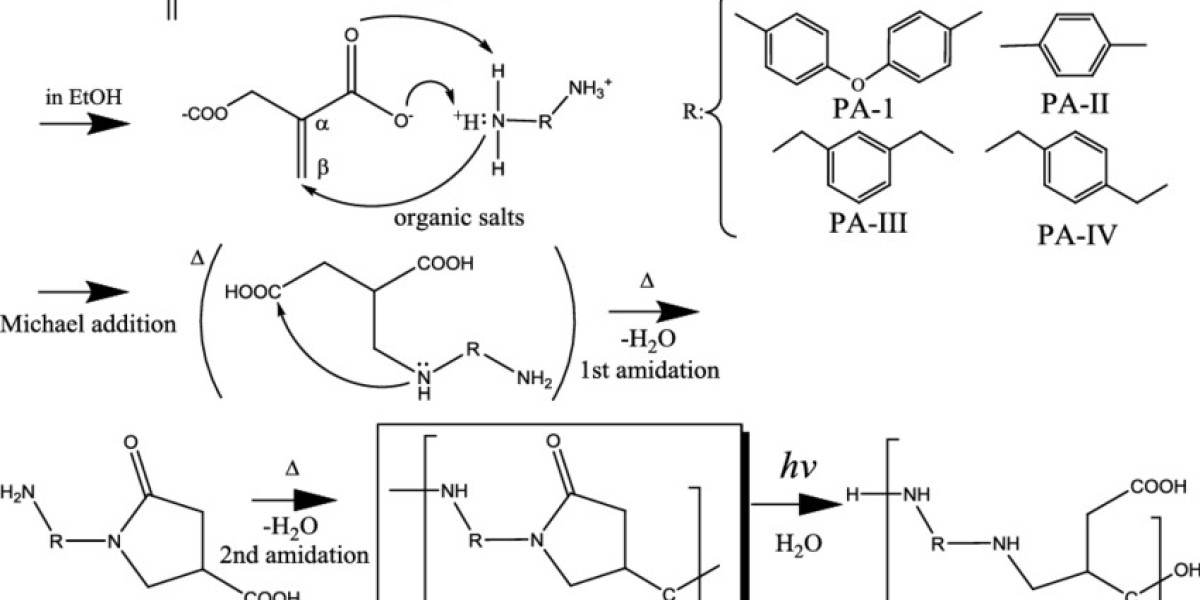
Bio-polyamide refers to a type of polyamide (commonly known as nylon) that is produced from renewable biomass sources instead of conventional petrochemicals. Polyamides are known for their durability, strength, and abrasion resistance, making them essential in various industrial and consumer applications.
The Bio-Polyamide market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.5% from 2024 to 2034. Following this trajectory, the market is projected to reach USD 924.75 million by 2034, up from an estimated value of USD 238.68 million in 2024.
Request Sample Copy: https://wemarketresearch.com/sample-request/bio-polyamide-market/1512
Sustainable Production of Bio-Polyamide
Bio-polyamides are derived from plant-based feedstocks like castor oil, corn, or other biomass materials. Unlike traditional polyamides that rely heavily on fossil fuels, bio-polyamides contribute t o lower environmental impact by minimizing greenhouse gas emissions and reducing dependency on non-renewable resources.
Leading Companies in the Bio-Polyamide Market
Evonik Industries AG
Ascend Performance Materials Inc.
Ube Industries, Ltd.
Arkema S.A.
Lanxess AG
Honeywell International, Inc.
SK Group
Radici Partecipazioni SpA
Huntsman Corporation
BASF SE
Key Market Drivers
Environmental Benefits:
The primary driver behind bio-polyamide adoption is its potential to reduce the carbon footprint associated with traditional polymers by using renewable resources such as castor oil or corn.
Regulations and Incentives:
Governments and regulatory bodies are introducing standards and incentives to promote the use of eco-friendly materials. Restrictions on certain chemicals and petrochemical-based polymers further accelerate the shift toward bio-polyamides.
Growing Consumer Demand for Sustainability:
Consumers are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly products, encouraging industries to adopt sustainable materials like bio-polyamide. Companies across sectors are exploring bio-based polymers to align with these preferences.
Technological Advancements:
Innovations in polymer chemistry and bioengineering have enabled more efficient production of bio-polyamides. Advances in biotechnology, such as enzymatic polymerization and green chemistry techniques, improve material performance while minimizing environmental impact.
Broad Application Scope:
Bio-polyamide’s versatility allows for extensive use across industries, including automotive, textiles, packaging, electronics, and consumer goods. The increasing exploration of new markets and applications drives further growth.
Challenges in the Bio-Polyamide Market
High Production Costs:
Bio-polyamide production can be more expensive than traditional petrochemical-based alternatives, impacting its widespread adoption.
Supply Chain Constraints:
Limited availability of bio-based feedstocks and disruptions in the supply chain pose challenges for manufacturers seeking consistent production capacity.
Emerging Trends and Opportunities
Sustainability and Environmental Awareness:
With rising environmental concerns, industries are shifting away from petroleum-based polymers to minimize their environmental impact and meet regulatory demands.
Technological Progress in Manufacturing:
New processes, such as green chemistry methods and enzymatic polymerization, are improving the efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and performance of bio-polyamide production.
Diverse Applications Across Industries:
The adoption of bio-polyamide is expanding across automotive, packaging, textiles, and electronics sectors to meet sustainability goals and consumer preferences for eco-friendly products.
Collaboration Across the Value Chain:
Strategic partnerships between feedstock suppliers, chemical manufacturers, and end-users are fostering innovation and facilitating market expansion. Joint ventures enable technology transfer, resource sharing, and growth opportunities.
Focus on Circular Economy:
There is increasing interest in developing bio-polyamide materials aligned with circular economy principles, encouraging closed-loop recycling and waste reduction.
Consumer Education and Awareness:
Raising awareness about the environmental benefits and performance advantages of bio-polyamide through marketing campaigns, product labeling, and certification programs will be critical to driving market acceptance and adoption.
Conclusion
The bio-polyamide market is set to witness substantial growth as industries and consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability. With advancements in biotechnology and polymer chemistry, along with regulatory support, bio-polyamides are becoming a viable alternative to petrochemical-based polymers. Despite challenges related to cost and supply chain, the market presents significant opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and expansion.