Chickenpox is a viral infection that many of us have heard about during childhood, often associated with itchy spots and days off from school. It is a very common infection, affecting anyone, young or old. However, its complications can affect individuals of any age. On the other hand, molluscum contagiosum is a frequently occurring skin infection caused by a virus with the same name. It usually shows up as small, raised, painless bumps on the skin. It can be more of a worry for kids and people with weak immune systems.
What is chickenpox and molluscum contagiosum?
Chickenpox is an infectious illness triggered by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), part of the herpes virus family. It mostly affects children, but adults can contract it too. Typically, individuals recover in roughly one or two weeks. However, it can result in severe issues, particularly for infants, pregnant women, and those with immunocompromised systems.
Molluscum contagiosum, known as ‘water warts,’ is a common skin infection that spreads easily. It causes tiny, elevated bumps on the skin, called ‘Mollusca.’ This infection often thrives in places where people are in close contact, like schools or during sports. While it is usually harmless and does not lead to serious health issues, the bumps can be itchy and may bother some people because of their appearance.
Symptoms and causes
Chickenpox typically begins with general uneasiness. The early symptoms include fatigue, muscle or joint aches, low-grade fever (usually under 102°F or 39°C), loss of appetite, headache, cough or runny nose, initial rashes, blisters, and scabs. Chickenpox spreads easily through the air when someone coughs, sneezes, or touches the fluid from their blisters.
Once inside the body, the virus remains in the respiratory tract. It can be transmitted roughly one to two days before the rash develops and will continue until all the blisters have formed a crust.
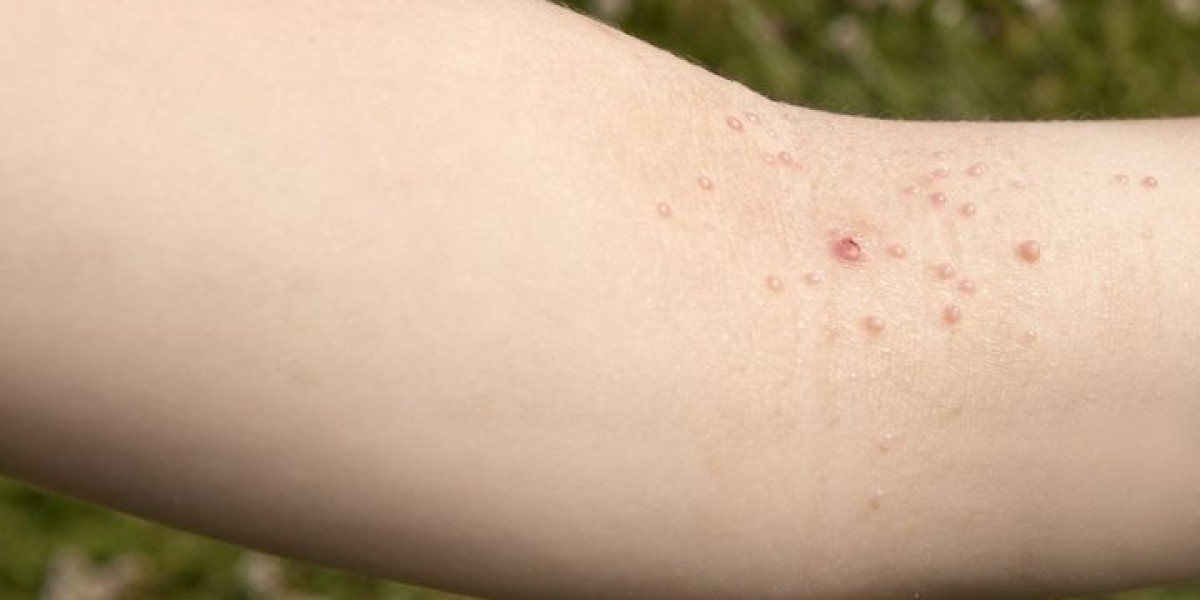
A person suffering from molluscum contagiosum develops small, pearl-like lesions, dimples in the centre, itchy bumps, and inflammation. They appear on the face, neck, arms, legs, genitals, abdomen, and inner thighs, usually two to eight weeks after virus exposure. Bumps are usually painless but can become sore or swollen with scratching. Lesions typically resolve within six to 18 months, but some may take longer to clear.
The causal agent belongs to the poxvirus family, the molluscum contagiosum virus. When IT enters the body, it causes small bumps or papules to form on the skin. These can spread to other body parts, making them contagious.
Prevention tips
You can prevent chickenpox by avoiding infected individuals and practising good hygiene, such as washing your hands regularly. To prevent molluscum contagiosum, you need to avoid skin-to-skin contact, sharing personal items, keeping hands clean, covering affected areas, and performing safe sex.
Conclusion
By understanding the symptoms, causes, and preventive measures, individuals can effectively manage these conditions while reducing the risk of transmission to others.