When it comes to diagnosing medical conditions accurately, biopsy for diagnostic purposes (خزعة لأغراض التشخيص) is one of the most reliable methods available. This procedure involves collecting a small sample of tissue or cells from the body to examine it under a microscope. Whether it’s to detect cancer, infections, or other diseases, biopsies play a critical role in modern medicine. In this blog, we’ll explore everything you need to know about biopsy for diagnostic purposes, including its types, benefits, and what to expect during the procedure.
What Is a Biopsy?
Definition and Purpose
A biopsy is a medical procedure where a small sample of tissue or cells is removed from the body for examination. It is primarily used for diagnostic purposes to identify diseases, infections, or abnormalities.
Why Is It Important?
Biopsies help doctors make accurate diagnoses, which are crucial for determining the right treatment plan. They are often used to confirm or rule out conditions like cancer, inflammation, or infections.
Types of Biopsies
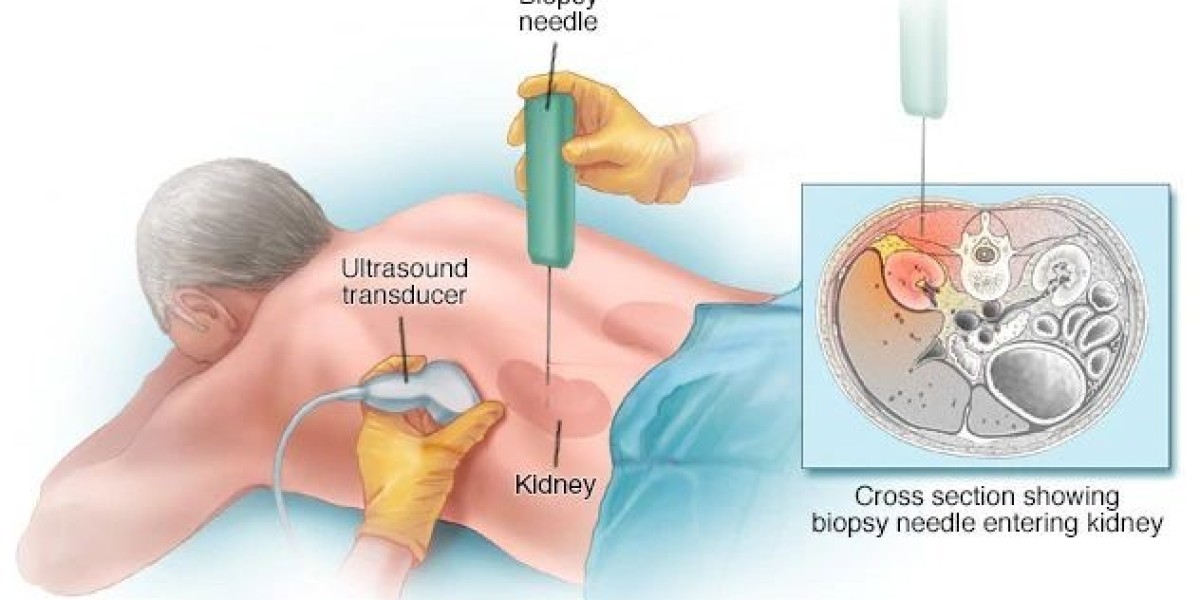
Needle Biopsy
This is a minimally invasive procedure where a thin needle is used to extract tissue or fluid from the body. It’s commonly used for breast, thyroid, or liver biopsies.
Surgical Biopsy
In this type, a small incision is made to remove a tissue sample. It’s often used when a larger sample is needed for accurate diagnosis.
Endoscopic Biopsy
During an endoscopy, a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the body to collect tissue samples from internal organs like the stomach or lungs.
Skin Biopsy
This involves removing a small sample of skin to diagnose conditions like rashes, infections, or skin cancer.
Why Is Biopsy for Diagnostic Purposes Necessary?
Accurate Diagnosis
A biopsy provides detailed information about the tissue or cells, helping doctors identify the exact nature of a disease.
Early Detection
Early diagnosis through a biopsy can significantly improve treatment outcomes, especially in cases of cancer.
Customized Treatment Plans
The results of a biopsy help doctors tailor treatment plans to the patient’s specific condition, ensuring better results.
How Is a Biopsy Performed?
Preparation
Before the procedure, patients may need to avoid certain medications or fasting, depending on the type of biopsy.
The Procedure
The process varies based on the type of biopsy. Local anesthesia is often used to minimize discomfort.
Post-Procedure Care
After the biopsy, patients may experience mild pain or swelling. Proper care, such as keeping the area clean, is essential to prevent infections.
Benefits of Biopsy for Diagnostic Purposes
High Accuracy
Biopsies provide highly accurate results, making them a gold standard for diagnosing many conditions.
Minimally Invasive Options
Many biopsy techniques, like needle biopsies, are minimally invasive and require little recovery time.
Comprehensive Insights
The detailed analysis of tissue samples helps doctors understand the severity and progression of a disease.
Risks and Considerations
Potential Risks
While biopsies are generally safe, there are some risks, such as bleeding, infection, or damage to nearby tissues.
When to Avoid a Biopsy
In some cases, such as severe bleeding disorders, a biopsy may not be recommended. Always consult your doctor to assess the risks.
What to Expect After a Biopsy
Recovery Time
Most biopsies have a short recovery period, with patients resuming normal activities within a day or two.
Interpreting Results
The tissue sample is sent to a lab for analysis, and results are typically available within a few days to a week.
Follow-Up
Depending on the results, further tests or treatments may be recommended.
Common Myths About Biopsies
Myth 1: Biopsies Are Always Painful
While some discomfort is possible, most biopsies are performed under local anesthesia, minimizing pain.
Myth 2: Biopsies Spread Cancer
There is no evidence to suggest that biopsies cause cancer to spread.
Myth 3: Biopsies Are Only for Cancer
Biopsies are used to diagnose a wide range of conditions, not just cancer.
FAQs About Biopsy for Diagnostic Purposes
1. Is a biopsy painful?
Most biopsies are performed under local anesthesia, so patients may feel slight discomfort but not severe pain.
2. How long does it take to get biopsy results?
Results typically take a few days to a week, depending on the complexity of the analysis.
3. Are there any risks associated with a biopsy?
While rare, risks include bleeding, infection, or damage to nearby tissues. Your doctor will discuss these with you beforehand.
4. Can a biopsy diagnose all types of diseases?
Biopsies are highly effective for diagnosing many conditions, but they may not be suitable for every situation. Your doctor will recommend the best diagnostic approach.
Conclusion
A biopsy for diagnostic purposes is a vital tool in modern medicine, offering accurate and detailed insights into various medical conditions. Whether it’s for detecting cancer, infections, or other abnormalities, biopsies help doctors provide the best possible care. By understanding the types, benefits, and process of a biopsy, you can approach the procedure with confidence and clarity. If you have any concerns or questions, always consult your healthcare provider to ensure you’re making informed decisions about your health.