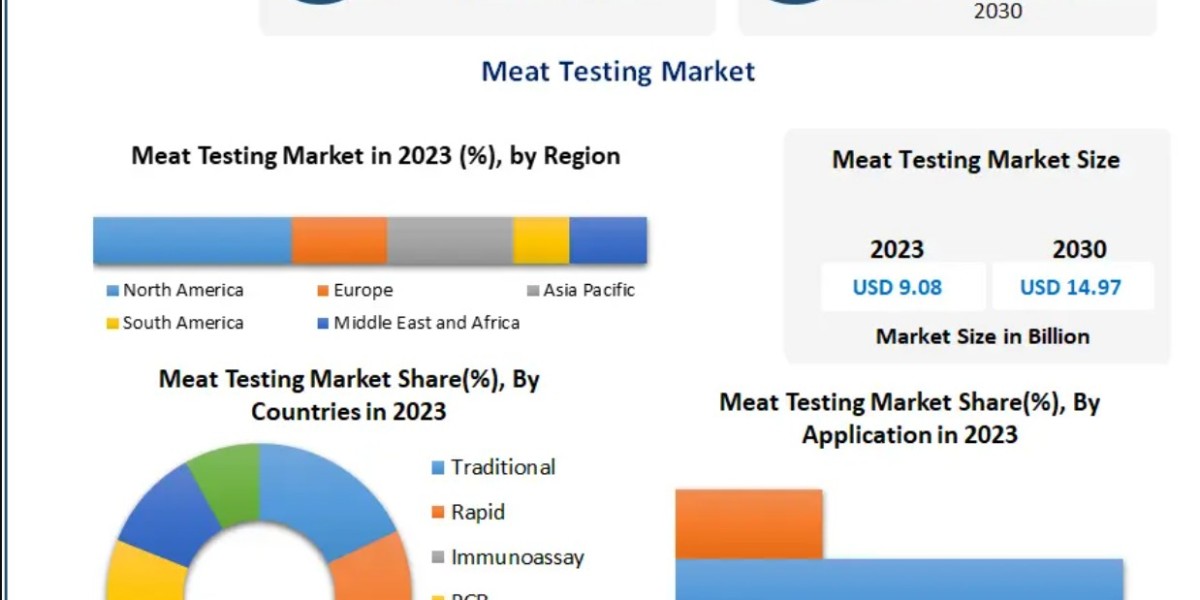
Global Meat Testing Market size was valued at USD 9.08 Bn. in 2023 and the total Meat Testing revenue is expected to grow by 7.4 % from 2024 to 2030, reaching nearly USD 14.97 Bn.
Meat Testing Market Overview:
Maximize Market Research is a Business Consultancy Firm that has published a detailed analysis of the “ Meat Testing Market”. The report includes key business insights, demand analysis, pricing analysis, and competitive landscape. The analysis in the report provides an in-depth aspect at the current status of the Meat Testing Market.
Download your sample copy of this report today! https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/request-sample/11187/
Meat Testing Market Scope and Methodology:
The Meat Testing Market requires a mix of both qualitative and quantitative research methods. Meat Testing Market information is gathered through different research methods including expert advice, primary and secondary research, both qualitative and quantitative. Primary research gathers important data from interviews, surveys, questionnaires, and input from industry experts, customers and other sources either in person or over the phone.
The report provides in-depth analysis on different strategies used by leading companies, such as partnerships, mergers, acquisitions, and collaborations. The report conducted a SWOT analysis to evaluate the company's market position through identifying its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Analytical techniques, such as examining investment returns, conducting a feasibility study, and using Porter's five forces analysis, were employed to assess the Meat Testing market. The bottom-up approach was used to determine the global and regional Meat Testing market sizes.
Meat Testing Market Regional Insights:
The Meat Testing Market report is segmented into various key countries. Countries such as North America (United States, Canada, Mexico), Europe (United Kingdom, Germany, France, Spain, Italy, Rest of Europe), Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, Australia, South Korea, ASEAN countries, other APAC countries), South America (Brazil), and the Middle East and Africa.
Secure your sample copy of this report immediately!https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/request-sample/11187/
Meat Testing Market Segmentation:
by Target Tested
Pathogens
Species identification
GMOs
Allergens
Mycotoxins
Heavy metals
Veterinary drug residues
Others (pesticide and chemical residues)
by Sample Type
Meat
Poultry
Pigmeat
Beef
Sheep and goat meat
Others (camel, rabbit, horse, venison, and wild boar)
Seafood
by Technology
Traditional
Rapid
Immunoassay
PCR
Chromatography
Spectroscopy
Meat Testing Market Key Players:
1. Microbac Laboratories - United States
2. Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. - United States
3. FoodChain ID Group Inc. - United States
4. Genetic ID - United States
5. Certified Laboratories - United States
6. NEOGEN Corporation - United States
Obtain your sample copy of this report now!https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/request-sample/11187/
Key questions answered in the Meat Testing Market are:
- What is Meat Testing ?
- What is the growth rate of the Meat Testing Market?
- Which are the factors expected to drive the Meat Testing Market growth?
- What are the upcoming opportunities and trends for the Meat Testing Market?
- Who are the leading companies and what are their portfolios in Meat Testing Market?
- What are the recent industry trends that can be implemented to generate additional revenue streams for the Meat Testing Market?
- Who are the key players in the Meat Testing Market?
- What are the different segments of the Meat Testing Market?
- Which is the fastest growing region in the Meat Testing Market?
- What growth strategies are the players considering to increase their presence in Meat Testing ?
- What is the CAGR at which the Meat Testing Market will grow during the forecast period?
- What segments are covered in the Meat Testing Market?
To learn more about the findings of this research, please check:https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/meat-testing-market/11187/
Key Offerings:
- Past Market Size and Competitive Landscape
- Past Pricing and price curve by region
- Market Size, Share, Size & Forecast by different segment
- Market Dynamics – Growth Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, and Key Trends by Region
- Market Segmentation – A detailed analysis by segment with their sub-segments and Region
- Competitive Landscape – Profiles of selected key players by region from a strategic perspective
- Competitive landscape – Market Leaders, Market Followers, Regional player
- Competitive benchmarking of key players by region
- PESTLE Analysis
- PORTER’s analysis
- Value chain and supply chain analysis
- Legal Aspects of Business by Region
- Lucrative business opportunities with SWOT analysis
- Recommendations
Our Trending Related Report :
Global Atopic Dermatitis Drugs Market https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-atopic-dermatitis-drugs-market/23907/
Global Southern Blotting Market https://www.maximizemarketresearch.com/market-report/global-southern-blotting-market/87676/
About Maximize Market Research:
Maximize Market Research is a multifaceted market research and consulting company with professionals from several industries. Some of the industries we cover include medical devices, pharmaceutical manufacturers, science and engineering, electronic components, industrial equipment, technology and communication, cars and automobiles, chemical products and substances, general merchandise, beverages, personal care, and automated systems. To mention a few, we provide market-verified industry estimations, technical trend analysis, crucial market research, strategic advice, competition analysis, production and demand analysis, and client impact studies.
Contact Maximize Market Research:
3rd Floor, Navale IT Park, Phase 2
Pune Banglore Highway, Narhe,
Pune, Maharashtra 411041, India
sales@maximizemarketresearch.com
+91 96071 95908, +91 9607365656