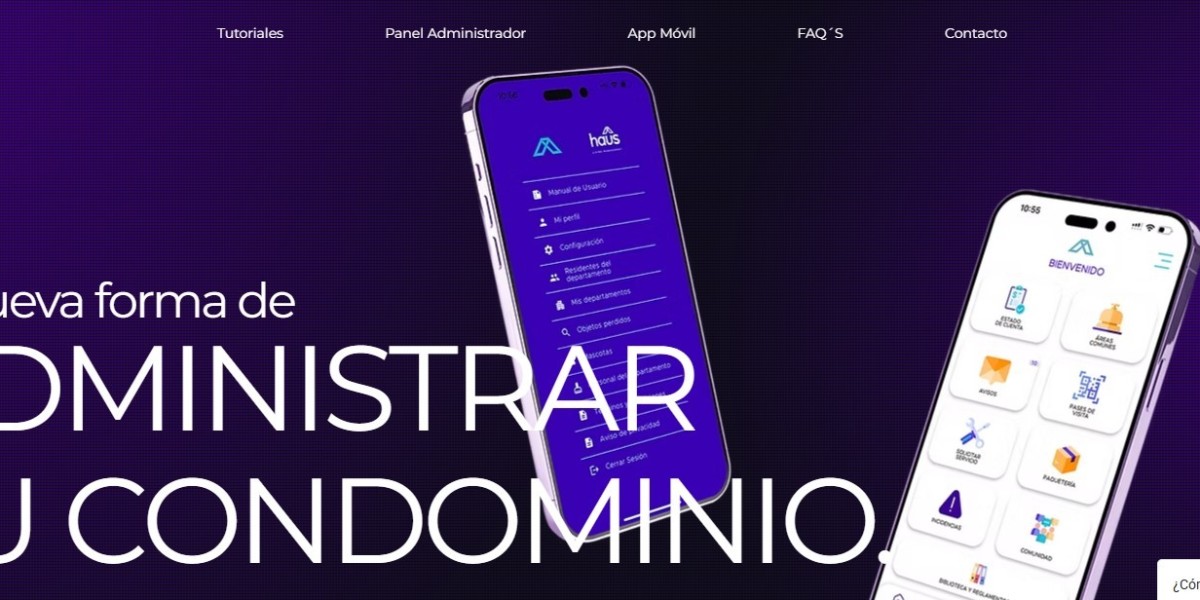
La administración de condominios puede ser una tarea compleja. Entre pagos de mantenimiento, comunicación con residentes, control de servicios, y organización de espacios comunes, los administradores suelen enfrentarse a múltiples desafíos que consumen tiempo y esfuerzo. En este contexto surge la app administración de condominios, una herramienta digital innovadora que transforma la manera en la que se gestionan comunidades residenciales y edificios modernos.
¿Qué es una App de Administración de Condominios?
Una app administración de condominios es una aplicación móvil o plataforma digital diseñada para centralizar y simplificar las tareas administrativas de un condominio. Permite a los administradores y residentes conectarse en un mismo sistema, agilizando procesos como pagos en línea, notificaciones, gestión de incidencias, reservas de áreas comunes y más.
En pocas palabras, es una solución tecnológica que mejora la transparencia, la comunicación y la eficiencia en la gestión comunitaria.
Principales Funcionalidades
Las aplicaciones de administración de condominios ofrecen una amplia gama de herramientas que se adaptan a las necesidades de cada comunidad. Entre las más destacadas se encuentran:
Gestión de pagos y cuotas: permite a los residentes pagar su mantenimiento mensual o cuotas especiales en línea, reduciendo la morosidad.
Reportes de incidencias: los usuarios pueden reportar problemas de mantenimiento o seguridad directamente desde la app.
Reservas de áreas comunes: gimnasios, salones de eventos, canchas deportivas o piscinas pueden gestionarse de manera organizada y transparente.
Comunicación interna: envío de notificaciones, avisos importantes o circulares directamente a los residentes.
Control contable: generación de reportes financieros que facilitan el trabajo del administrador y aumentan la confianza de los propietarios.
Beneficios para Administradores y Residentes
El uso de una aplicación para administración de condominios no solo facilita el trabajo del administrador, sino que también mejora la experiencia de los residentes.
Transparencia: todos los pagos, reportes y gastos quedan registrados de manera accesible para la comunidad.
Ahorro de tiempo: tanto administradores como vecinos evitan trámites físicos y largas reuniones.
Accesibilidad: la información está disponible 24/7 desde cualquier dispositivo móvil.
Mejor convivencia: al optimizar la comunicación, se reducen los conflictos y malentendidos.
Eficiencia operativa: las tareas repetitivas se automatizan, lo que permite una gestión más profesional.
La Importancia de Digitalizar la Gestión de Condominios
En la actualidad, las comunidades buscan soluciones modernas que se adapten al estilo de vida digital. Una app administración de condominios no solo agiliza procesos, sino que también da un valor agregado a la propiedad, generando confianza y mejorando la calidad de vida de quienes habitan el edificio o conjunto residencial.
Además, al centralizar toda la información en un solo lugar, se evita la pérdida de datos y se mantiene un historial claro de pagos, incidencias y comunicaciones.
Conclusión
La app administración de condominios es más que una herramienta tecnológica: es una solución integral para comunidades que buscan eficiencia, transparencia y comodidad. Su implementación convierte la gestión tradicional en un proceso moderno, rápido y accesible, beneficiando tanto a administradores como a residentes.
En un mundo cada vez más digital, contar con una aplicación de este tipo ya no es un lujo, sino una necesidad para garantizar una convivencia armónica y bien organizada dentro de cualquier condominio.