In the current, evolving landscape, many individuals face challenges related to vitality, endurance, and sexual function due to stress, aging, or hormonal imbalances. Fortivir Max Capsules is a dietary supplement formulated to naturally bolster male vitality, elevate testosterone levels, and enhance physical and sexual productivity. With a robust combination of herbal extracts and amino acids, Fortivir Max Male Enhancement aims to help men reclaim their confidence, vitality, and endurance.
➢ ➢ Fortivir Max Male Enhancement ➢ ➢ Get Exclusive Offers on Official Website - Upto 57% off in USA, UK, Ireland, Australia, Canada & New Zealand
What is Fortivir Max Capsules?
The Fortivir Max assessment of the product is rational and justified, taking into account that the company is evidently prepared to distribute it to every targeted professional, enabling them to experience the benefits of the essential noise reduction process. No harmful side effects or undesirable synthetic substances were utilized in the formulation of this product. With the assistance of Fortivir Max Capsules, you will no longer need to wait for sexual satisfaction. The remarkable ingredients that make up the blend have all been confirmed to enhance libido, virility, and erection size. The richness and efficacy of the formulation have been validated through clinical and practical testing. You can manage your success and confidence post-intercourse by employing this solution.
How Does Fortivir Max Capsules Work?
Fortivir Max Capsules functions by addressing the root causes of male performance issues: low testosterone levels, inadequate blood circulation, and insufficient stamina. Here’s how it assists:
Supports Testosterone Production: Fortivir Max Capsules comprises ingredients that stimulate the body's natural testosterone production, crucial for muscle growth, libido, and overall vitality.
Improves Blood Flow: Enhanced blood circulation to the penile chambers promotes firmer, longer-lasting erections.
Enhances Nitric Oxide Levels: By increasing nitric oxide production, Fortivir Max Capsules facilitates the relaxation of blood vessels, aiding in superior nutrient and oxygen delivery throughout the body.
Boosts Energy and Endurance: It contains adaptogenic herbs and natural stimulants that raise energy levels, reduce fatigue, and improve performance both in the gym and the bedroom.
➢ ➢ Fortivir Max Male Enhancement ➢ ➢ Get Exclusive Offers on Official Website - Upto 57% off in USA, UK, Ireland, Australia, Canada & New Zealand
Benefits of Fortivir Max Male Enhancement:
Improved Sexual Performance: Promotes stronger, more sustained erections.
Increased Libido & Desire: Stimulates natural sexual arousal and interest.
Enhanced Stamina: Raises energy levels for better physical and intimate performance.
Supports Muscle Growth: May aid in increasing strength and lean muscle mass through testosterone support.
Greater Confidence: Improved performance can lead to enhanced self-esteem and satisfaction.
How to Use Fortivir Max:
Using Fortivir Max Capsules is simple:
1. Take 2 capsules daily with a generous glass of water.
2. For optimal results, take consistently at the same time each day.
3. Pair with a nutritious diet, regular exercise, and adequate hydration for maximum efficacy.
➢ ➢ Fortivir Max Male Enhancement ➢ ➢ Get Exclusive Offers on Official Website - Upto 57% off in USA, UK, Ireland, Australia, Canada & New Zealand
Expected Results:
Some users report increased energy and an enhanced mood within the first week. More noticeable effects, such as improved performance and stamina, typically emerge after 2–4 weeks of consistent use. Continued use may lead to better muscle tone, libido, and long-term sexual health benefits.
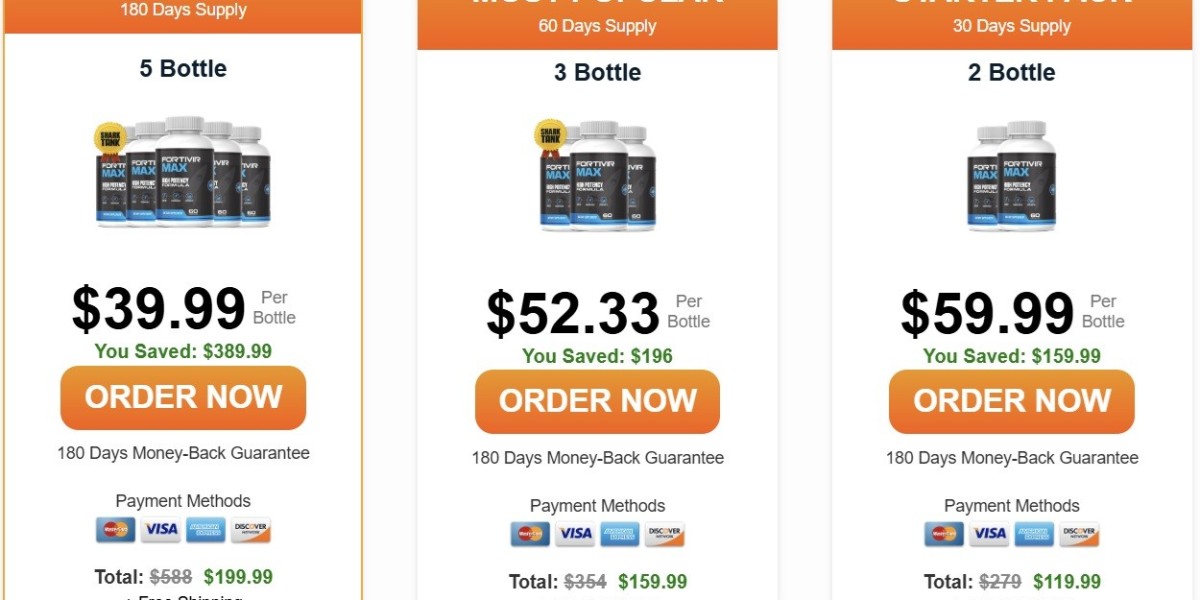
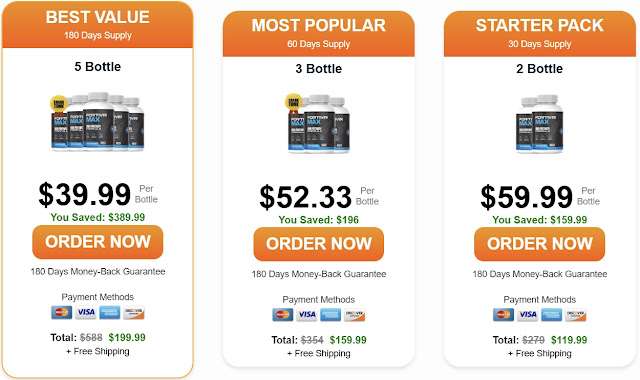
Where to Buy Fortivir Max Capsules USA, CA, UK, AU, NZ, IE?
Fortivir Max Capsules is available exclusively online through the official website. Purchasing directly ensures you receive an authentic product along with exclusive offers such as bulk discounts, complimentary shipping, and a money-back guarantee. Fortivir Max Male Enhancement Avoid unauthorized sellers to protect against counterfeit supplements.