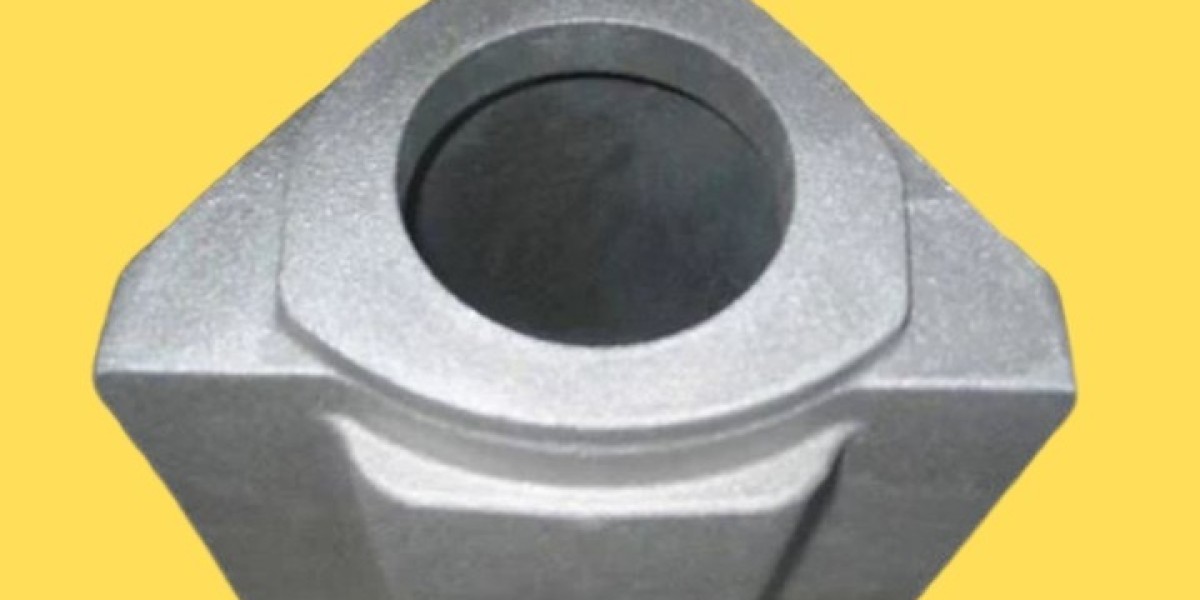
White cast irons are a remarkable class of materials renowned for their exceptional strength, hardness, and wear resistance. Despite their popularity in various industrial applications, many remain unfamiliar with their properties and uses. In this guide, we delve into the intricacies of white cast irons, exploring their composition, properties, applications, and advantages.
Composition: White cast irons are primarily composed of iron and carbon, with carbon content typically ranging from 2.0% to 4.0%. Unlike gray cast iron, white cast irons contain little to no graphite, resulting in a predominantly white fractured surface upon failure. Additionally, alloying elements such as chromium, manganese, and nickel are often added to enhance specific properties like corrosion resistance and toughness.
Properties:
- Hardness: White cast irons exhibit exceptional hardness, making them suitable for applications where abrasion resistance is critical. Their hardness typically ranges from 450 to 700 Brinell hardness number (BHN), surpassing that of many other engineering materials.
- Wear Resistance: Thanks to their microstructure consisting of hard carbides embedded in a tough matrix, white cast irons offer outstanding wear resistance, prolonging component lifespan in abrasive environments.
- Strength: With high carbon content and carbide formation, white cast irons possess impressive strength, enabling them to withstand heavy loads and impact.
- Brittleness: While white cast irons boast remarkable hardness and wear resistance, they tend to be brittle, making them susceptible to sudden failure under certain conditions.
Applications:
- Mining and Mineral Processing: White cast irons find extensive use in mining equipment such as crusher liners, slurry pumps, and grinding media due to their exceptional wear resistance.
- Metalworking Industry: Tools and components subjected to abrasive wear in metalworking processes benefit from the durability of white cast irons.
- Power Generation: Components in coal pulverizers, ash handling systems, and other high-wear applications in power plants often utilize white cast irons for their robustness.
- Construction Machinery: White cast irons are employed in construction machinery parts like excavator teeth, bucket lips, and wear plates to withstand abrasive materials encountered in construction sites.
Advantages:
- Exceptional Wear Resistance: White cast irons outperform many other materials in abrasive environments, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- High Hardness: Their hardness makes them ideal for applications requiring resistance to surface deformation and wear.
- Cost-Effective: Despite their superior properties, white cast irons can be a cost-effective solution in applications where prolonged service life outweighs initial material costs.
- Versatility: Their versatility allows for a wide range of applications across industries, offering solutions to diverse wear-related challenges.
Conclusion: White cast irons stand as stalwarts in the realm of engineering materials, prized for their unparalleled hardness, wear resistance, and strength. Understanding their composition, properties, applications, and advantages is crucial for engineers and designers seeking robust solutions in abrasive environments. With their versatility and exceptional performance, white cast irons continue to play a vital role in enhancing the durability and reliability of countless industrial components and machinery.