In modern construction and civil engineering projects, the need for strong and durable materials is critical, particularly when dealing with soil stabilization, road construction, and other infrastructure projects. One such material that plays a key role in enhancing the stability and longevity of these projects is biaxial geogrid. This innovative material is used to reinforce soils and improve load distribution in a variety of applications, including road construction, railways, embankments, and retaining walls. In this article, we will explore the importance, applications, and installation process of biaxial geogrid, as well as what to consider when selecting Geogrid manufacturers in India or any other region.
What is Biaxial Geogrid?
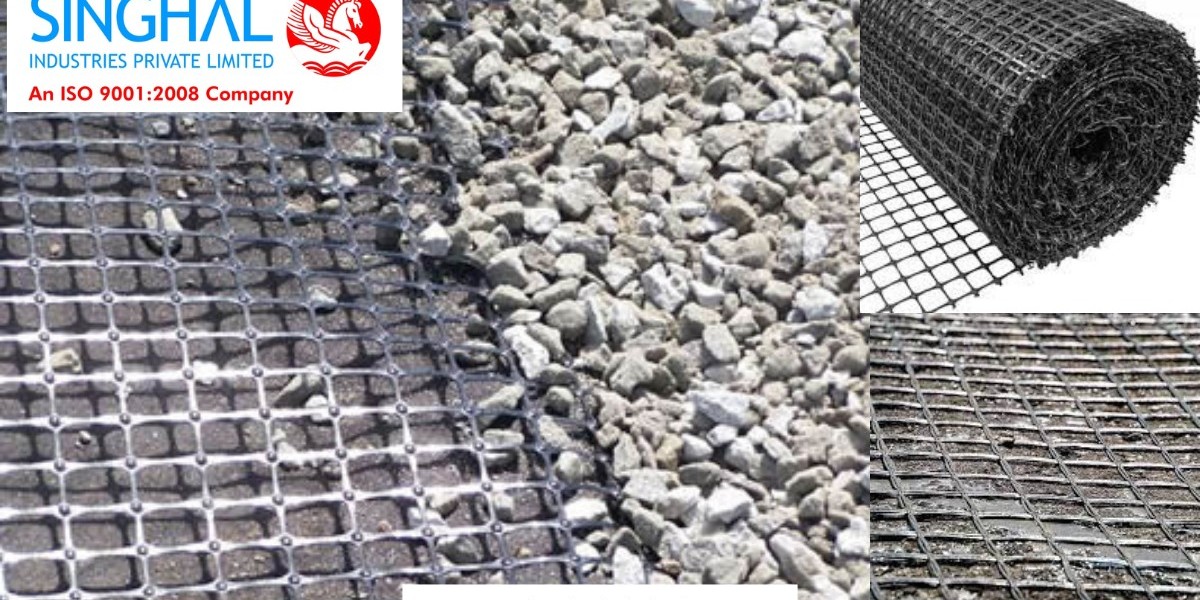
A biaxial geogrid is a type of geosynthetic material made from high-strength polymer fibers, such as polypropylene or polyester, that are woven or knitted into a grid-like structure. This structure provides strength and stability to the soil or aggregate it is applied to. The term "biaxial" refers to the geogrid’s ability to provide reinforcement in both the machine and cross-machine directions, meaning it can resist stresses in multiple directions.
Biaxial geogrids are often used in applications where soil stability needs to be improved, such as in road construction, base stabilization, or slope reinforcement. They are primarily designed to improve the load-bearing capacity of soil by interlocking with the soil particles and providing lateral confinement. This ensures that the soil does not shift or erode over time, even under heavy loads.
Benefits of Biaxial Geogrid
Enhanced Load Distribution: Biaxial geogrid helps to distribute the applied load more evenly across a larger area. This reduces the risk of soil failure, making it particularly useful in projects like road construction or railway embankments.
Soil Stabilization: Biaxial geogrid helps to stabilize loose, soft, or weak soils by increasing the shear strength of the soil. The geogrid acts as a reinforcement element, preventing excessive settlement and maintaining the integrity of the structure.
Cost-Effective Solution: By reducing the need for deep excavations or expensive soil treatments, biaxial geogrid provides a cost-effective solution for soil stabilization and reinforcement. It can significantly lower construction costs while improving the performance of the underlying soil.
Durability and Longevity: Biaxial geogrids are made from durable materials that are resistant to environmental conditions like UV rays, moisture, and temperature variations. This enhances the longevity of the construction and reduces the need for maintenance.
Easy Installation: The installation of biaxial geogrid is relatively simple and can be completed quickly, reducing the overall construction timeline. It can be easily laid over prepared soil, compacted, and covered with aggregate materials to achieve the desired results.
Applications of Biaxial Geogrid
Biaxial geogrid is used in various engineering and construction applications. Some of the most common uses include:
Road and Highway Construction: Biaxial geogrids are widely used in the construction of roads, highways, and airfields to reinforce the base layers and improve load distribution. They help to prevent rutting and settlement caused by traffic load and reduce the thickness of the aggregate required for construction.
Railway Embankments: In railway construction, biaxial geogrids are used to stabilize the embankments and prevent differential settlement under the weight of the trains. The grid structure helps maintain the integrity of the embankment, reducing the risk of erosion or collapse.
Slope Reinforcement: Biaxial geogrids are often used to stabilize slopes, prevent soil erosion, and enhance the structural stability of embankments or retaining walls. The geogrid helps to reduce the potential for landslides and improve the overall performance of the slope.
Landfills and Waste Management: In landfill projects, biaxial geogrids are used to provide soil reinforcement and prevent lateral movement of the waste materials. This helps to maintain the integrity of the landfill and prevents seepage of contaminants into the surrounding environment.
Bridge Approaches: Biaxial geogrid is often used in the construction of bridge approaches to improve the stability of the ground and prevent settlement, ensuring that the bridge remains structurally sound over time.
Biaxial Geogrid Installation
Biaxial geogrid installation is a straightforward process, but it requires careful planning to ensure that the material functions effectively. The installation process generally involves the following steps:
Site Preparation: Before installing biaxial geogrid, the site must be properly prepared. This involves clearing debris, leveling the ground, and ensuring the soil is compacted and stable. The surface should be free from large rocks, vegetation, or any other material that could interfere with the geogrid’s performance.
Geogrid Placement: Once the site is prepared, the geogrid is rolled out over the soil. The biaxial geogrid should be aligned properly, ensuring that it is placed flat and free of wrinkles or folds. The geogrid should also be positioned so that its edges overlap with adjacent sheets by at least a few inches.
Securing the Geogrid: After the geogrid is placed, it is typically anchored at the edges or along the perimeter of the project area. In some cases, geogrids may be secured using stakes, pins, or other methods to ensure that they remain in place during the construction process.
Covering with Aggregate: Once the geogrid is secured, a layer of aggregate material, such as crushed stone or gravel, is spread over the top of the geogrid. This layer is compacted to ensure a strong bond between the geogrid and the underlying soil. The aggregate layer also helps to protect the geogrid from damage during construction.
Final Compaction: The final step in Biaxial geogrid installation involves compacting the surface material to ensure proper soil stabilization. The compaction process helps to ensure that the geogrid remains firmly in place and that the soil is reinforced.
Choosing the Right Geogrid Manufacturers
When selecting geogrid manufacturers, it’s important to look for companies that offer high-quality products and can provide expert advice on installation and application. If you are based in India or looking for geogrid suppliers in this region, choosing Geogrid manufacturers in India who have a proven track record in providing durable, high-performance geogrids will ensure the success of your project.
Reputable geogrid manufacturers will provide detailed product specifications, including tensile strength, elongation, and compatibility with various soil types. They will also offer custom solutions tailored to your specific project needs, ensuring that the geogrid selected meets the performance requirements of your site.
FAQs About Biaxial Geogrid
1. How does biaxial geogrid differ from uniaxial geogrid?
Biaxial geogrid provides reinforcement in both the machine direction and cross-machine direction, offering strength in multiple directions. Uniaxial geogrids, on the other hand, only provide reinforcement in one direction, making them suitable for different applications where strength in a single direction is sufficient.
2. Can biaxial geogrids be used in all soil types?
Yes, biaxial geogrids can be used in a variety of soil types, including sandy, clayey, and gravelly soils. The specific choice of geogrid will depend on the soil conditions and the load requirements of the project.
3. Are there any environmental concerns with biaxial geogrid?
Biaxial geogrids are made from durable polymer materials that are resistant to environmental conditions such as UV radiation, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. However, it is important to ensure that the geogrid is properly disposed of or recycled after use to minimize environmental impact.