The ecosystem,made up of sellers,merchants,acquirers,and various third-party payment service providers,fosters and drives the development of diverse payment methods and acceptance models,integrating various approaches into payment networks.Traditionally,acquirers and merchants have been the primary participants in the international acceptance ecosystem.However,with the evolution of different business scenarios,many other entities now play critical roles in facilitating the growth of the acceptance business.These entities may be specialized companies providing payment and value-added services to sellers,or professional organizations offering technical services to acquirers.We can categorize these entities as Intermediary Professionals.
These Intermediary Professionals offer unique advantages:
For Consumers:They provide a wider range of convenient payment options tailored to different regions or customer segments or focus on resolving consumer disputes.
For Sellers or Merchants:They deliver services tailored to the distinct needs of large,medium,small,and micro merchants,offering industry-specific payment solutions.They may specialize in a particular aspect of payments,such as gateway services or seller platform development.
For Acquirers:They help expand the pool of eligible sellers by bringing long-tail merchant clients into specific payment acceptance models.They can also provide specialized technical services.
For Technology Partners:Some entities offer integrated solutions for electronic payment acceptance capabilities.
In today’s international acceptance ecosystem,the roles of various participants are relatively well-defined.Leading international card networks like VISA,Mastercard,American Express,and Discover have already outlined key qualification requirements,rights,and responsibilities for the main participants in this ecosystem through their rules.This article summarizes and categorizes these roles and responsibilities.
Functions and Entities in the International Payment Acceptance Ecosystem
1. Acquirers
Acquirers are entities authorized by international card schemes or other clearing entities to conduct merchant acquiring activities.They bear the obligations and responsibilities associated with acquiring.Acquirers sign contracts with merchants or payment facilitators,provide cash payments to cardholders,or deposit funds into prepaid cards,and directly or indirectly facilitate transaction processing.
Acquirers are required to accept transactions only from digital wallet operators,merchants,marketplace merchants,and sponsored merchants supported by payment facilitators within their jurisdiction and submit them for processing.Except as otherwise required by local laws and regulations or specific international card scheme rules,acquirers must only accept transactions from merchant outlets located within their own country or region.Although payment facilitators can help acquirers expand long-tail merchants and acquirers may assist in processing transactions for merchants supported by digital wallet operators,acquirers hold the ultimate responsibility for managing these merchants,including risk and fund management.Acquirers must not only manage the behavior of end merchants but also ensure that payment facilitators,digital wallet operators,and marketplace merchants operate in compliance with regulations.
2. Merchants
Generally,merchants are sellers that enter contracts with acquirers.Merchants can sign directly with acquirers,or in the international payment acceptance ecosystem,they can sign through payment facilitators,with the acquirer contracting with the payment facilitator to accept various payment methods.Merchants are the entities recognized by customers as selling products or services,typically identifiable by their brand or business name.Merchants are also responsible for managing customer relationships,such as handling refunds or disputes. ONERWAY Global payment services
To determine whether an entity is a merchant or another intermediary,the following questions can be considered:
i. From whom does the customer believe they are purchasing goods or services?
ii. Does the entity own the goods or services being sold?
iii. Is the entity’s primary income derived from selling goods or services rather than from commissions or fees?
iv. Does the entity provide customer service and handle refunds?
3. Marketplace Merchants
Marketplace merchants are entities that enable,manage,or host third-party sellers on their online platforms(such as e-commerce websites or mobile apps),accepting card payments or other payment instruments for these sales."Third-party sellers"are individuals or entities offering physical goods or digital products for sale on consumer-facing online platforms but do not directly accept card payments themselves.Sellers on marketplace platforms can either operate within the same industry or across multiple sectors.Marketplace merchants and acquirers must be located in the same country or region,although third-party sellers on these platforms can be in different areas.
4. Payment Facilitators(PF or PayFac)
Payment facilitators,also known as"Master Merchants"or"Merchant Aggregators,"are third-party service providers.They can sign merchant acceptance agreements on behalf of acquirers(subject to local laws and international card scheme rules)and receive settlement funds from acquirers on behalf of their supported sub-merchants(Sponsored Merchants).Entities that perform either of these functions can be classified as payment facilitators,and many perform both.Under certain conditions,payment facilitators can also process transactions as a gateway between acquirers and sellers and provide POS infrastructure.Payment facilitators must obtain payment licenses in their respective regions and have the capacity and qualifications to process payment services.
Payment facilitators typically operate in two business models:one specializes in offering payment acceptance services for small sellers or highly specialized industries with unique needs(e.g.,rent payments,education,or government payments).The other model includes service providers offering a range of services,including payment products and fund settlement,as value-added services to sellers.
5. Independent Sales Organizations(ISOs)
ISOs collaborate with acquirers to engage in various activities,including solicitation,sales,customer service,seller training,and marketing of POS terminals,mPOS devices,or other acceptance solutions offered by acquirers.ISOs operate as agents for acquirers,meaning that when sellers sign service agreements with ISOs,they are effectively contracting with the acquirers.While ISOs may sell or resell gateway services alongside merchant account products from acquirers,they do not process transactions,receive settlement funds,or have access to seller customer data or transaction processing environments.If an ISO processes transactions or intends to do so,it would be classified as another type of third-party service provider.
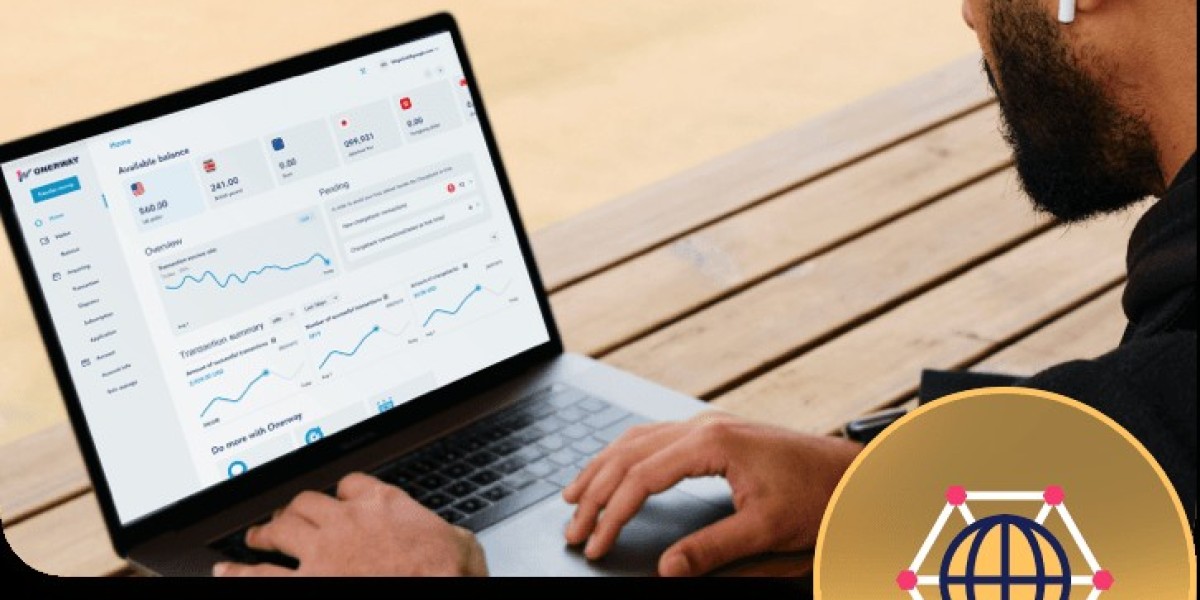
ONERWAY holds licenses such as EMI in the UK,MSB in the US,and MSO in Hong Kong.It has passed PCI-DSS Level Certification and is one of the principal members of Visa and Mastercard.
ONERWAY's compliant operational model provides a high level of security for users'funds.By combining its proprietary intelligent risk control system with third-party risk control systems,it greatly enhances transaction security,reduces the risk of fraud,and strives to deliver a comprehensive one-stop cross-border payment solution and service.
Article source:ONERWAY(https://www.onerway.com)
Search
Popular Posts