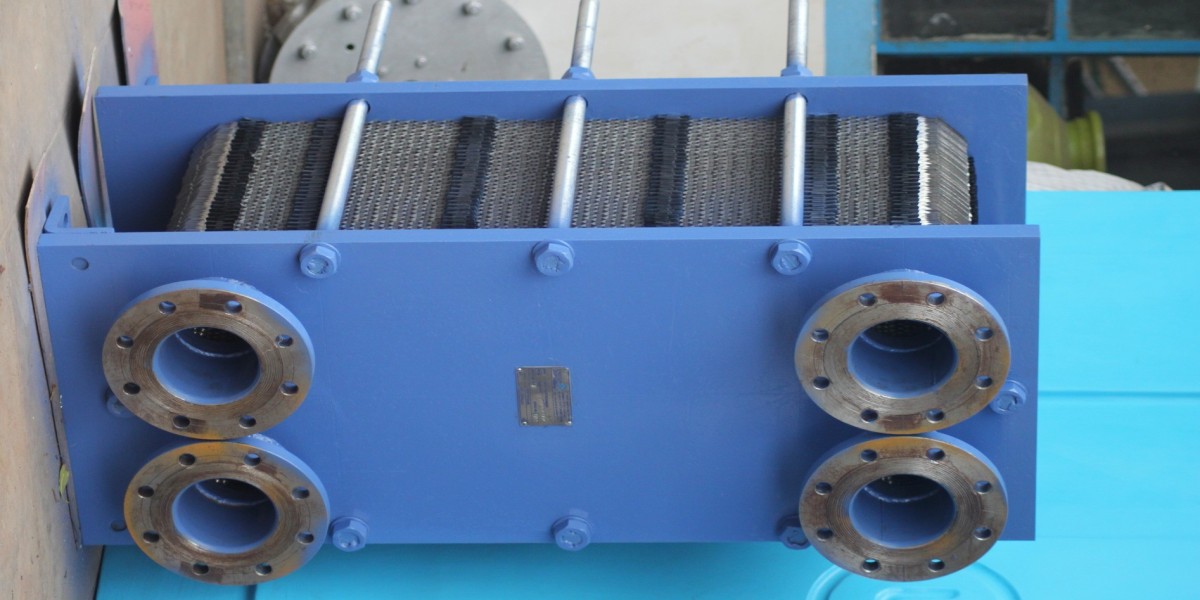
What is a Plate-Type Heat Exchanger?
A plate-type heat exchanger is a device designed to transfer heat between two or more fluids without mixing them. It consists of a series of thin, corrugated plates arranged in a frame. These plates create parallel channels for the fluids to flow through, allowing heat exchange across the plate surface. The design maximizes the surface area for heat transfer while maintaining compactness.
How Does it Work?
The operation of a plate-type heat exchanger is straightforward yet highly effective:
Fluid Flow: Hot and cold fluids enter alternating channels formed by the plates.
Heat Transfer: Heat transfers from the hotter fluid to the colder fluid through the plates.
Exit: The fluids exit the exchanger at their respective outlets, with the colder fluid gaining heat and the hotter fluid losing heat.
Gaskets or welded seals ensure that the fluids do not mix and flow through the intended channels.
Types of Plate Heat Exchangers
Gasketed Plate Heat Exchangers: Flexible and easy to maintain, these use gaskets to seal the plates and guide fluid flow.
Brazed Plate Heat Exchangers: Compact and durable, these are sealed by brazing the plates together, making them ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications.
Welded Plate Heat Exchangers: Designed for demanding environments, these eliminate gaskets, offering resistance to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals.
Semi-Welded Plate Heat Exchangers: Combine gasketed and welded designs to balance flexibility and durability.
Key Advantages
Plate-type heat exchangers offer several benefits:
High Efficiency: Their large surface area and thin plate construction ensure excellent heat transfer rates.
Compact Design: They are smaller and lighter than shell-and-tube heat exchangers for the same capacity.
Scalability: Plates can be added or removed to adjust capacity, making them adaptable to varying demands.
Easy Maintenance: Gasketed designs allow for quick disassembly and cleaning.
Energy Savings: Efficient heat transfer reduces energy consumption and operational costs.
Applications Across Industries
Plate-type heat exchangers find applications in diverse fields:
HVAC Systems: For heating, ventilation, and air conditioning processes.
Food and Beverage: For pasteurization, cooling, and heating.
Chemical Processing: To handle corrosive fluids and maintain precise temperature control.
Power Generation: In cooling systems and waste heat recovery.
Marine and Automotive: For engine cooling and lubrication oil heating.
Considerations for Use
While plate-type heat exchangers are highly efficient, certain factors should be considered:
Fouling: Regular cleaning is necessary to prevent performance degradation due to fouling.
Pressure Drop: The intricate design can cause higher pressure drops compared to other exchangers.
Material Selection: The plates must be made of materials compatible with the fluids being used to prevent corrosion.
Initial Cost: The upfront cost can be higher, but this is often offset by long-term savings in energy and maintenance.
Conclusion
Plate-type heat exchangers are a cornerstone of modern thermal engineering, providing unmatched efficiency and versatility. Their ability to adapt to a wide range of applications and environments makes them a preferred choice for engineers and designers. By understanding their design and operation, industries can leverage these devices to enhance processes, save energy, and achieve sustainability goals.
Whether you're optimizing a manufacturing process or designing a sustainable HVAC system, plate-type heat exchangers are a smart investment in energy efficiency and performance.