Precision casting, also known as investment casting or lost-wax casting, is a versatile and intricate manufacturing process used to create high-quality metal components with complex geometries. This guide will walk you through the entire process of Precision casting, from pattern creation to finishing touches, providing valuable insights and tips along the way.
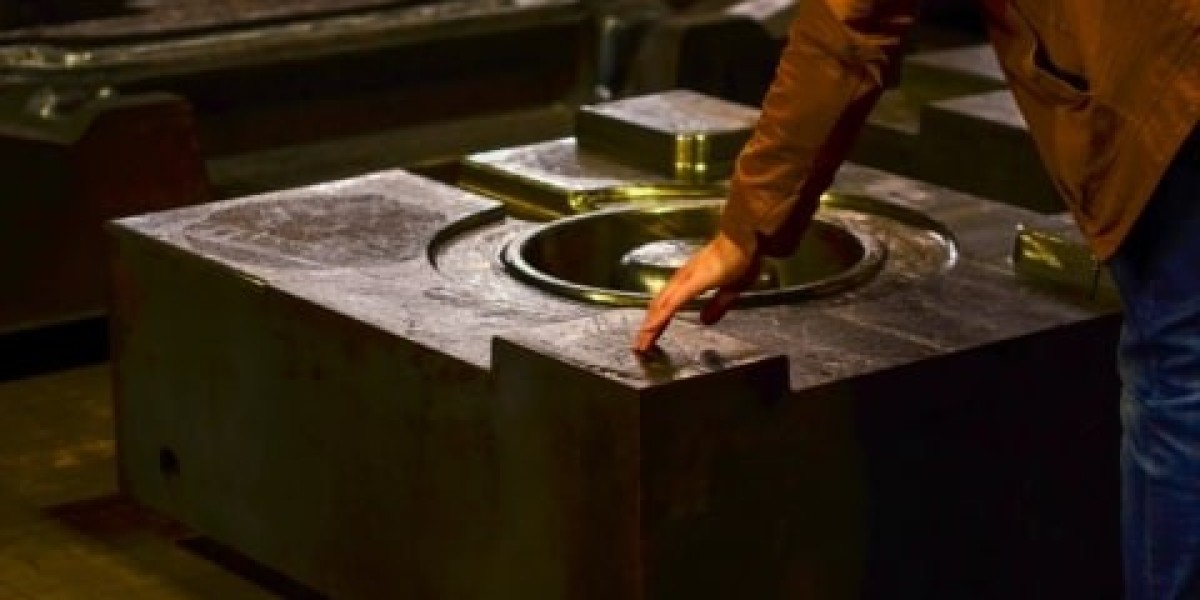
Understanding Precision Casting: Precision casting is a process where a wax pattern is coated with a refractory material to create a mold. Once the mold is formed, the wax is melted and drained, leaving behind a cavity. Molten metal is then poured into the mold, filling the cavity and forming the desired part.
Pattern Creation: The first step in precision casting is creating a pattern of the desired part. This can be done using various materials such as wax, plastic, or even metal. The pattern should be an exact replica of the final part, including all intricate details and features.
Assembly of Patterns: Multiple patterns can be assembled onto a single wax sprue to form a cluster, which facilitates the casting process by allowing multiple parts to be cast simultaneously.
Investment (Mold) Making: The assembled patterns are then coated with a ceramic slurry and covered with a refractory material, such as silica sand, to create the mold. This process is repeated multiple times to build up a thick and durable mold.
De-Waxing: Once the mold is complete, it is heated to melt and drain the wax, leaving behind a hollow cavity in the shape of the desired part. This step is crucial for removing any residual wax and preparing the mold for metal casting.
Preheating the Mold: Before pouring molten metal into the mold, it is preheated to a specific temperature to prevent thermal shock and ensure proper flow of the metal.
Metal Casting: The preheated mold is filled with molten metal, which is poured into the cavity through a gating system. The metal is allowed to solidify within the mold, taking the shape of the pattern.
Cooling and Solidification: After casting, the mold is allowed to cool, allowing the metal to solidify completely. This process may take several hours depending on the size and complexity of the part.
Mold Breakout: Once the metal has solidified, the mold is broken away to reveal the cast part. Any excess metal or imperfections are removed through machining or other finishing processes.
Finishing Touches: The cast part undergoes various finishing processes such as grinding, polishing, and surface treatments to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Quality Control: Throughout the entire precision casting process, strict quality control measures are implemented to ensure the final parts meet the required specifications. This includes dimensional inspections, material testing, and visual inspections.
Applications of Precision Casting: Precision casting is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, jewelry, and medical equipment manufacturing, where complex and high-quality metal components are required.
By following this detailed guide, you can master the art of Precision casting and produce high-quality metal parts with intricate designs and precise dimensions. Remember to pay close attention to each step of the process and continuously strive for perfection in your casting endeavors.