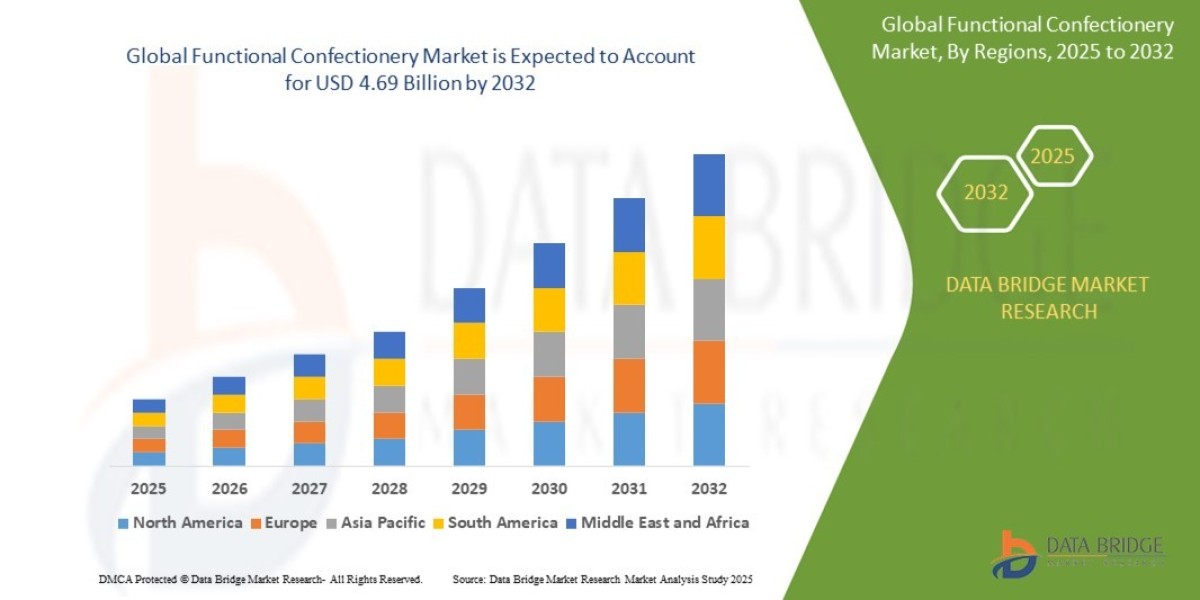
The European electric vehicles (EV) market has emerged as one of the fastest-growing automotive segments globally, driven by technological innovation, environmental concerns, and government policies promoting clean transportation. In recent years, electric mobility has shifted from being a niche alternative to becoming a mainstream choice for consumers and businesses. The region’s commitment to carbon neutrality, coupled with advancements in charging infrastructure, battery technology, and vehicle design, is accelerating the transition toward an electrified transport ecosystem.
Market Outlook
Europe’s EV market is experiencing robust growth as countries strengthen climate policies and promote sustainable transport. Government incentives, subsidies, and tax benefits are encouraging both manufacturers and consumers to adopt electric vehicles. This shift is not limited to passenger cars; commercial vehicles, buses, and even two-wheelers are undergoing electrification. Countries like Norway, Germany, France, and the Netherlands are leading the adoption curve, with increasing EV penetration in their automotive markets.
Technological Advancements Driving Adoption
The rapid progress in battery technology is a key driver for EV adoption in Europe. Modern lithium-ion batteries now offer greater energy density, longer lifespans, and shorter charging times, making electric vehicles more practical for everyday use. Additionally, the development of solid-state batteries holds the promise of even higher efficiency and safety in the near future.
Vehicle manufacturers are integrating advanced features such as regenerative braking, connected car technology, and AI-powered driving assistance systems to make EVs more appealing to tech-savvy consumers. The rise of modular EV platforms also enables automakers to design multiple vehicle types using a single scalable architecture, reducing production costs and accelerating new model launches.
Charging Infrastructure Expansion
One of the most crucial aspects of EV adoption in Europe is the development of a widespread and reliable charging infrastructure. Public and private investments are fueling the installation of fast-charging stations across highways, urban areas, and workplaces. Many countries are working toward ensuring that charging points are easily accessible, reducing range anxiety for potential buyers.
Innovations such as ultra-fast chargers, wireless charging systems, and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology are also gaining traction, enabling EVs to not only consume but also supply energy back to the grid during peak demand periods.
Environmental and Policy Support
The European Union has set ambitious climate goals, including a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 and achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. Transportation accounts for a substantial portion of CO₂ emissions, making electrification a vital strategy. Regulations are pushing for the phase-out of internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles in the coming decades, creating a favorable environment for EV adoption.
Countries are offering incentives such as purchase rebates, reduced registration fees, and exemptions from congestion charges. These measures not only make EVs more affordable but also enhance their attractiveness over conventional vehicles.
Consumer Trends and Market Demand
Consumer preferences in Europe are shifting toward sustainability, energy efficiency, and innovative mobility solutions. Younger generations, in particular, are more open to electric mobility, viewing it as both environmentally responsible and technologically advanced. The rise of car-sharing services, ride-hailing platforms, and subscription-based EV ownership models is further broadening access to electric vehicles.
The growing availability of various EV models—ranging from compact city cars to luxury SUVs—ensures that there is an option for every lifestyle and budget. This diversification is crucial in driving adoption across different consumer segments.
Challenges and Future Scope
Despite the rapid growth, certain challenges remain in the European EV landscape. These include the high upfront cost of electric vehicles, dependence on imported raw materials for battery production, and the need for standardization across charging networks. Moreover, ensuring grid stability as EV adoption rises is a concern for energy providers.
However, these challenges also present opportunities. Localizing battery production, investing in renewable energy integration, and developing advanced recycling methods for EV batteries can strengthen Europe’s position in the global electric mobility market. As technology matures and economies of scale are achieved, EV prices are expected to drop, making them accessible to a broader audience.
The Road Ahead
The future of electric vehicles in Europe looks promising, with continuous innovation and policy support shaping the industry’s trajectory. Collaborations between automakers, technology companies, and energy providers will be essential in building a cohesive EV ecosystem. As autonomous driving technology evolves, its integration with electric mobility could redefine transportation altogether.
By the mid-2030s, EVs are expected to dominate new vehicle sales in Europe. With ongoing investments in infrastructure, battery research, and renewable energy, the region is well-positioned to lead the global shift toward sustainable transportation.
Conclusion
The Europe electric vehicles market is at the forefront of a transformative era in mobility. Driven by environmental imperatives, supportive policies, and technological advancements, the region is steadily moving toward a zero-emission future. While challenges persist, the momentum is undeniable. As innovation continues and consumer awareness grows, electric vehicles are set to become the cornerstone of Europe’s transportation landscape—ushering in a cleaner, smarter, and more sustainable future.