Introduction to the Gurley Porosity Testing Method
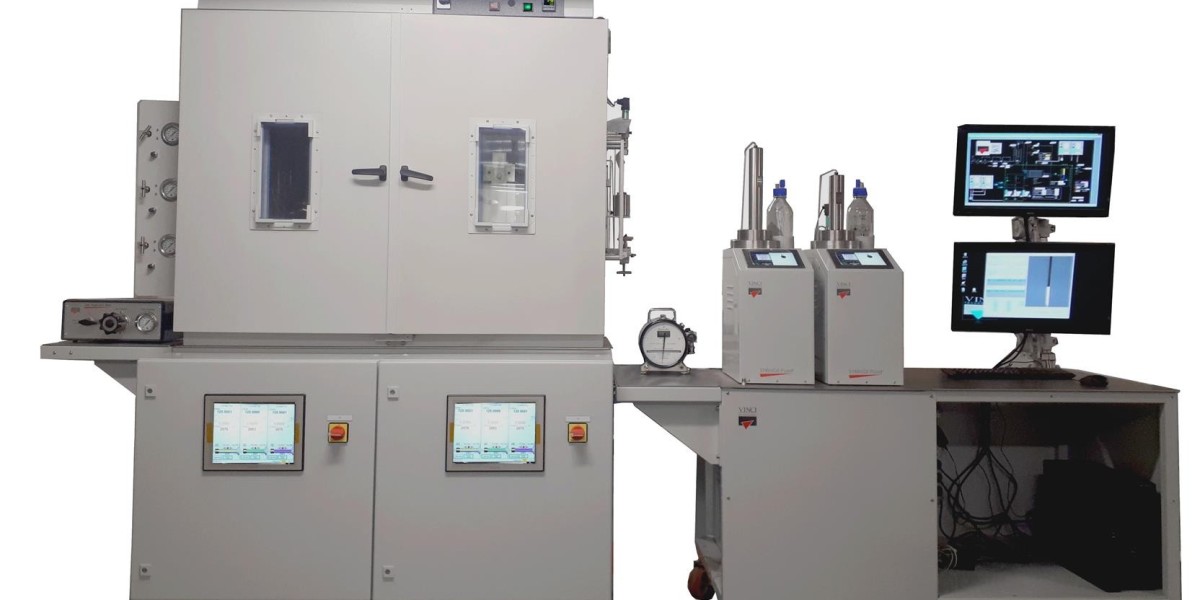
The Gurley method is a widely used technique for measuring the porosity of materials, particularly paper, textiles, and other porous substrates. The test provides critical insights into the permeability of a material by determining how easily air can pass through it. Many industries rely on this method to ensure quality control, optimize production processes, and improve material performance. The gurley porosity tester is the primary device used to conduct this evaluation, offering standardized measurements that allow manufacturers to maintain consistency and reliability in their products.
Operational Principles of the Gurley Apparatus
The Gurley apparatus operates on the principle of controlled air flow through a material under a specific pressure. The tester consists of a cylindrical chamber, a weighted piston, and an airtight seal. A sample of the test material is securely placed over an air passage, and the apparatus is then sealed. As the weighted piston descends, it forces air through the sample, and the time required for a set volume of air to pass through is recorded. This duration is measured in Gurley seconds, with higher values indicating lower permeability and greater resistance to airflow. The method is particularly useful for evaluating materials used in filtration, packaging, and industrial membranes.
Step-by-Step Procedure of the Gurley Test
Performing the Gurley test involves a structured process to ensure accurate results. The first step is preparing the material sample according to standardized dimensions. The sample is then placed onto the test surface, ensuring a secure and even seal to prevent leakage. The tester’s piston is carefully set to a predetermined height, and the weight is released to allow air to pass through the material. The timer is activated simultaneously, and the duration required for a specific air volume to traverse the sample is measured.
The test is typically repeated multiple times to ensure consistency and eliminate anomalies. Environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity can influence porosity measurements, so controlled testing conditions are recommended. Some modern testers integrate automated features to enhance precision and reduce operator error.
Interpreting Results from Gurley Porosity Measurements
The primary outcome of the Gurley test is a numerical value indicating the material’s porosity. A lower Gurley number suggests higher permeability, meaning air passes through the material quickly. Conversely, a higher number indicates greater resistance to airflow, suggesting a denser or more tightly woven structure. These results are used to classify materials based on their suitability for specific applications.
For instance, in the paper industry, the Gurley porosity value helps determine whether a paper type is suitable for printing, filtration, or packaging. In the automotive sector, the method is used to evaluate gasket materials and ensure they meet required sealing properties. Understanding these results allows manufacturers to adjust production techniques, optimize raw materials, and maintain industry compliance.
Advantages and Limitations of the Gurley Method
The Gurley method offers several advantages, making it a preferred choice for many industries. One key benefit is its simplicity and ease of use, requiring minimal setup and training. The tester provides reliable and repeatable measurements, which are essential for maintaining quality control. Additionally, the method is cost-effective compared to more advanced permeability testing techniques.
However, the Gurley test also has some limitations. It is primarily suitable for materials with moderate porosity and may not be effective for extremely porous or impermeable substances. The test relies on the assumption of uniform material thickness, meaning variations in density can influence results. Furthermore, manual operation introduces potential inconsistencies, although automated versions of the gurley porosity tester can mitigate this issue. Despite these challenges, the method remains a valuable tool for assessing permeability in a wide range of materials.
Applications of Gurley Porosity Testing in Various Industries
The Gurley method is widely used across multiple industries due to its effectiveness in evaluating material porosity. In the paper and packaging sector, it helps manufacturers produce materials with consistent air permeability, ensuring optimal printing performance and protective qualities. Filtration industries rely on the test to measure the efficiency of air and liquid filters, ensuring they meet regulatory standards.
In the automotive and aerospace industries, the test is used to analyze the porosity of gasket materials, seals, and membranes. These components require precise porosity levels to ensure proper functionality and durability. Additionally, battery manufacturers use the Gurley test to assess separator materials, which impact the performance and longevity of energy storage systems.
Conclusion
The Gurley method remains an essential technique for evaluating material porosity across various industries. By utilizing a standardized approach, the gurley porosity tester provides accurate and repeatable results that contribute to quality control and product optimization. While the method has its limitations, its ease of use and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred choice for assessing permeability in materials such as paper, textiles, and industrial membranes. Understanding the significance of these measurements allows manufacturers to enhance material properties, improve performance, and meet industry requirements effectively.