In the world of laser technology, picosecond lasers stand out for their extraordinary speed and precision. Operating at pulse durations in the picosecond range (one trillionth of a second), these lasers offer unmatched accuracy, making them indispensable for a wide array of industries, from medical treatments to material processing. In this article, we explore how picosecond lasers work, their advantages, and how they compare to other laser technologies such as nanosecond lasers.
What is a Picosecond Laser?
A picosecond laser emits extremely short bursts of energy that last only a picosecond (1 picosecond = 1 trillionth of a second). The brief pulse duration enables these lasers to interact with materials at an incredibly fine level, making them ideal for precise cutting, engraving, and even medical procedures.
The Advantages of Picosecond Lasers
- Ultra-Precision: The extremely fast pulse duration of laser picosecond technology allows for exceptional precision, which is crucial in both medical and industrial applications.
- Minimal Heat Effect: Since the laser pulses are so short, the heat generated during interaction with the material is limited to the precise area of focus, reducing thermal damage. This feature is especially beneficial in medical treatments like tattoo removal and skin resurfacing.
- Minimal Side Effects: The rapid pulse duration ensures minimal disruption to surrounding tissues or materials, making picosecond laser technology safer and more effective than other types of lasers in delicate procedures.
Applications of Picosecond Lasers
Medical Treatments:
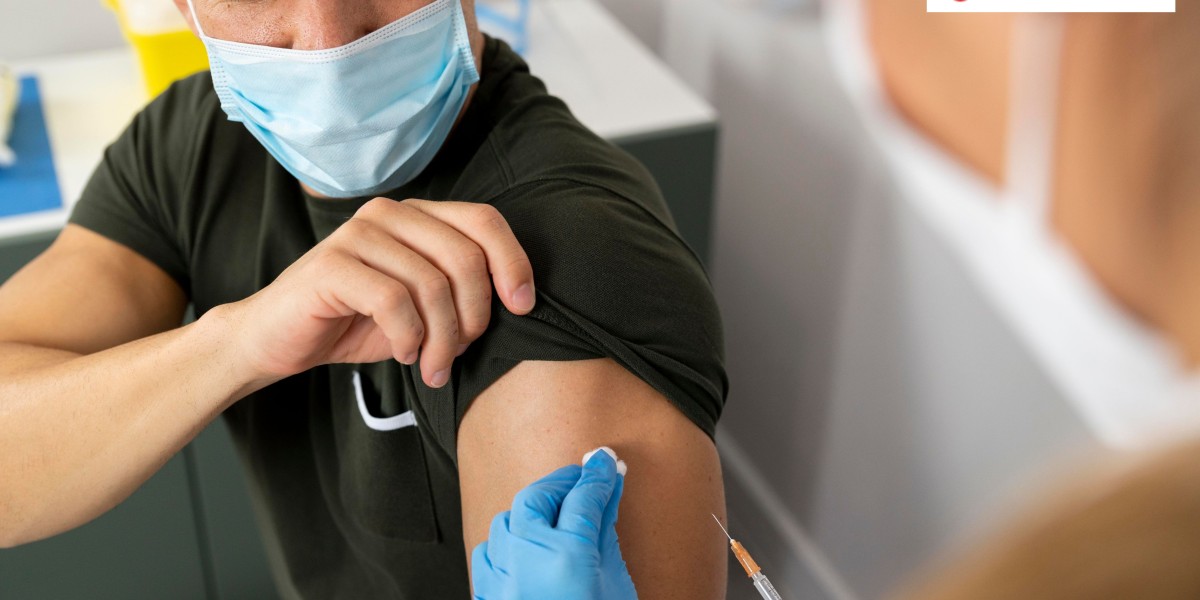
In dermatology, picosecond laser technology is used for non-invasive procedures like tattoo removal, skin rejuvenation, and the treatment of pigmentation. Its ability to break down ink particles in tattoos without damaging the skin is one of its most significant advantages.
Moreover, picosecond nanosecond lasers are also being explored in ophthalmology, offering enhanced precision for eye surgeries.Industrial Applications:
In industries such as material processing and micro-manufacturing, picosecond lasers are used for ultra-precise cutting and engraving. They can cut through metals, glass, and ceramics with little to no heat-affected zone, allowing for intricate designs and high-quality results.Scientific Research:
Picosecond lasers also play a crucial role in scientific research, particularly in fields like spectroscopy and chemical analysis. By capturing fast-moving processes at the picosecond level, scientists can study ultrafast molecular reactions, providing insights into everything from biological systems to quantum mechanics.
Picosecond vs. Nanosecond Lasers: Which is Better?
When comparing picosecond nanosecond lasers, the primary difference lies in the duration of the laser pulses. Picosecond lasers have shorter pulse durations, offering more precision and less heat diffusion, making them suitable for applications that require fine detailing. On the other hand, nanosecond lasers (with a pulse duration of one billionth of a second) are generally used for higher energy applications like laser marking and engraving.
Picosecond Laser: The Future of High-Precision Work
With continuous improvements in picosecond laser technology, these lasers are expected to become more widely adopted in various sectors, from high-precision surgery to advanced manufacturing. Their versatility, combined with cutting-edge performance, positions them as a crucial tool in future technological advancements.
Conclusion
Whether you're considering a picosecond laser for medical treatments, precision manufacturing, or scientific research, these lasers offer incredible advantages over traditional laser technologies. With unmatched precision, minimal heat effects, and the ability to handle delicate tasks, laser picosecond technology is revolutionizing industries worldwide.