Introduction
What drives people to do what they do? Why do some individuals chase success, while others simply strive for security? Abraham Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs provides a powerful framework for understanding human motivation, breaking it down into five essential levels. Let’s dive into this fascinating theory and see how it influences our lives today.
Who Was Abraham Maslow?
Abraham Maslow was an American psychologist best known for his work in humanistic psychology. In 1943, he introduced the concept of a “hierarchy of needs” in his paper, "A Theory of Human Motivation." His goal was to explain how human needs are prioritized and how they influence our behavior.
What is Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs?
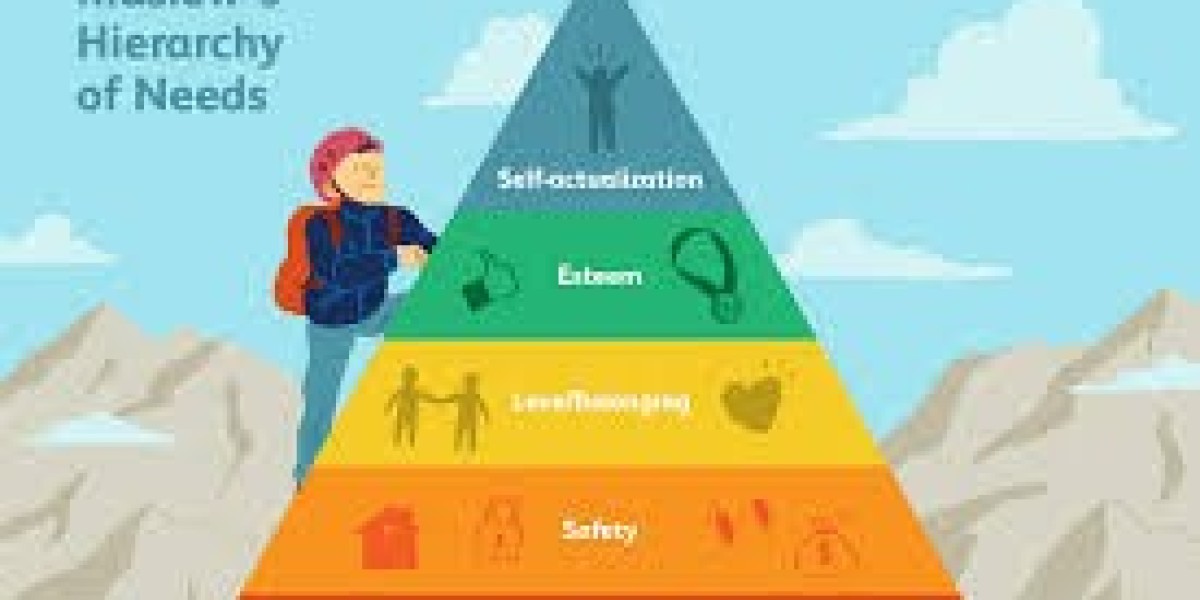
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs is a psychological theory that suggests human needs are arranged in a pyramid, with basic needs at the bottom and more complex needs at the top. People must fulfill lower-level needs before they can focus on higher-level growth and fulfillment.
The Five Levels of the Hierarchy
1. Physiological Needs (Basic Survival)
These are the most fundamental human needs, including:
Food and water
Shelter and sleep
Air and warmth
Without these necessities, it's almost impossible to focus on anything else.
2. Safety Needs (Security and Protection)
Once physiological needs are met, people seek safety, such as:
Physical security
Financial stability
Health and well-being
Think of how insurance or job security brings peace of mind.
3. Love and Belonging (Social Connections)
Humans are social creatures, and connections with others become vital. This includes:
Friendships and family bonds
Romantic relationships
Community and social groups
Loneliness or isolation can prevent people from moving up the hierarchy.
4. Esteem Needs (Recognition and Respect)
After feeling connected, people crave self-esteem and external validation. Key elements are:
Recognition and appreciation
Confidence and self-respect
Status and achievement
Without esteem, people may feel worthless or overlooked.
5. Self-Actualization (Achieving Full Potential)
At the top of the pyramid is self-actualization — the desire to become the best version of oneself. This involves:
Pursuing passions
Personal growth and creativity
Fulfilling one’s purpose
Understanding the Pyramid Structure
Maslow visualized these needs as a pyramid, with foundational needs at the base. You can't reach the peak without climbing the lower steps first.
Why the Order of Needs Matters
The sequence reflects the natural progression of human motivation. You can’t focus on relationships when you’re starving, and it’s hard to chase dreams without safety.
Real-Life Examples of Each Need
Physiological: Eating a meal when hungry
Safety: Locking your doors at night
Belonging: Joining a club or group
Esteem: Earning a promotion
Self-Actualization: Writing a novel or starting a charity
How Maslow's Theory Applies Today
From marketing strategies to mental health practices, Maslow’s theory remains widely relevant. Businesses, educators, and therapists use it to understand human behavior.
Criticisms and Limitations of the Theory
Critics argue the hierarchy is too rigid. People might seek love even without security, or pursue self-actualization despite unmet lower-level needs.
Modern Adaptations of Maslow's Hierarchy
Contemporary psychologists have adapted the model to include additional needs, like cognitive or aesthetic desires.
Maslow’s Theory in the Workplace
Companies use Maslow’s hierarchy to improve employee satisfaction, offering safety, belonging, and recognition to enhance productivity.
Education and Maslow’s Hierarchy
Teachers apply Maslow’s theory to create supportive environments, ensuring students’ basic and emotional needs are met for better learning.
Mental Health and Human Needs
Therapists use the hierarchy to help clients identify unmet needs, guiding them toward healing and growth.
Personal Growth and Self-Discovery
Understanding Maslow’s hierarchy can be a roadmap for personal development, helping individuals assess what’s missing and work toward fulfillment.
Conclusion
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs is a timeless guide to understanding human motivation. It shows that while we all have unique aspirations, our core needs are universal. By recognizing and addressing these needs, we can build more meaningful, fulfilling lives.
FAQs
1. Can people skip levels in Maslow’s hierarchy? Yes, people can sometimes prioritize higher-level needs, like creativity, even when basic needs aren’t fully met.
2. Is Maslow's hierarchy still relevant today? Absolutely! It remains a valuable framework in psychology, business, education, and personal development.
3. Can the hierarchy change for different cultures? Yes, cultural differences can influence how needs are prioritized. Some cultures may place community above individual achievement.
4. How do marketers use Maslow’s theory? Marketers tailor messages to appeal to different needs — from safety in insurance ads to self-actualization in luxury products.
5. What’s beyond self-actualization? Maslow later added a sixth stage: self-transcendence — the desire to connect with something greater than oneself, like spirituality or altruism.