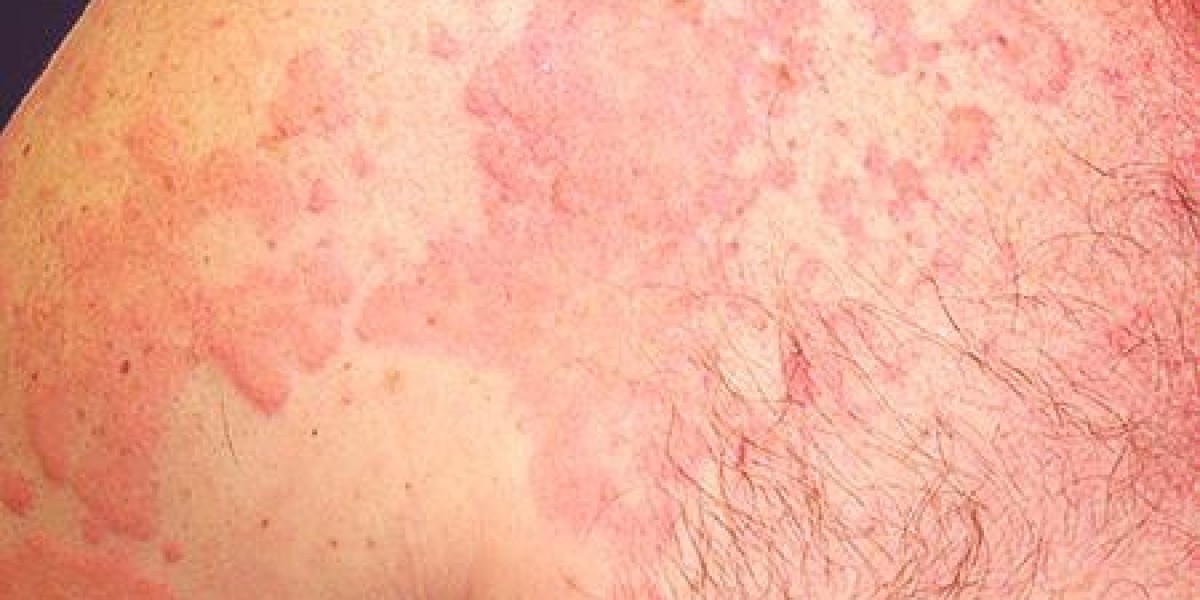
Hives, also known as urticaria, can be an irritating and persistent condition. While many people experience occasional hives due to allergies or environmental factors, some suffer from chronic hives, which last for six weeks or more and may have no identifiable cause. If your hives keep coming back, consulting hives specialists can help you identify triggers, manage symptoms, and find long-term relief.
What Are Chronic Hives?
Chronic hives, also called chronic urticaria, occur when itchy, red welts persist or frequently reappear for more than six weeks. Unlike acute hives, which are typically triggered by an allergic reaction, chronic hives may have underlying causes that are difficult to identify.
Types of Chronic Hives
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (CSU) – Hives appear without an obvious cause and can last for months or years.
- Chronic Inducible Urticaria – Hives are triggered by specific external factors, such as heat, cold, sunlight, pressure, or vibration.
Both types require specialized care from hives specialists to properly diagnose and manage symptoms.
What Causes Chronic Hives?
Unlike acute hives, which are commonly linked to allergens, the exact cause of chronic hives is often unknown. However, possible contributing factors include:
- Autoimmune disorders – Chronic hives are sometimes associated with lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, or thyroid disease.
- Infections – Viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections can lead to persistent hives.
- Hormonal imbalances – Thyroid disorders or hormonal changes may play a role in triggering hives.
- Medications – Some drugs, such as NSAIDs, antibiotics, and blood pressure medications, can cause hives.
- Environmental triggers – Heat, cold, pressure, or certain chemicals may contribute to chronic hives.
- Food sensitivities – While rare, some people with chronic hives may react to certain foods, preservatives, or additives.
If your hives persist despite eliminating common triggers, a hives specialist can help uncover the underlying cause and recommend effective treatment.
When Should You See a Hives Specialist?
Many people attempt to manage hives with over-the-counter antihistamines, but chronic hives require a professional evaluation. Here are signs that you should consult hives specialists:
1. Your Hives Last Longer Than Six Weeks
If your hives persist beyond six weeks, they are considered chronic. A specialist can determine whether they are related to an autoimmune disorder, infection, or unknown trigger.
2. Your Hives Keep Returning
Recurrent episodes of hives, even if they disappear temporarily, indicate a need for further medical investigation.
3. Over-the-Counter Medications Are Not Working
If antihistamines and home remedies are not providing relief, a specialist can prescribe stronger treatments tailored to your condition.
4. You Experience Severe Swelling (Angioedema)
Chronic hives accompanied by deep tissue swelling, especially around the lips, eyes, or throat, can be a sign of a more serious immune system reaction.
5. Your Hives Affect Your Daily Life
If hives interfere with your sleep, work, or overall quality of life, it’s time to seek expert care.
What to Expect When Visiting a Hives Specialist
When you visit a hives specialist, they will conduct a thorough evaluation, including:
- Medical History Review – Assessing any potential triggers, medications, and previous allergic reactions.
- Physical Examination – Evaluating the appearance, duration, and pattern of your hives.
- Diagnostic Tests – Depending on your symptoms, the specialist may recommend:
- Allergy testing (skin prick or blood test)
- Blood work to check for autoimmune conditions or thyroid issues
- Skin biopsy in rare cases to rule out other skin disorders
Based on the findings, the specialist will develop a personalized treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Chronic Hives
Managing chronic hives requires a comprehensive approach, including medications, lifestyle changes, and possible immunotherapy.
1. Antihistamines
- First-line treatment for hives that block histamine, the chemical responsible for allergic reactions.
- Non-drowsy options such as cetirizine, loratadine, and fexofenadine are often recommended.
- Higher doses may be prescribed for chronic cases.
2. Corticosteroids
- Short-term use of prednisone or other steroids may help with severe flare-ups.
- Not recommended for long-term treatment due to potential side effects.
3. Biologic Therapy (Omalizumab/Xolair)
- A targeted injection therapy that blocks the immune response causing chronic hives.
- Approved for individuals who do not respond to antihistamines.
- Offers long-term relief with minimal side effects.
4. Immunosuppressants
- In cases where chronic hives are linked to autoimmune diseases, drugs such as cyclosporine may be prescribed.
- Helps control the overactive immune system that may be triggering hives.
5. Lifestyle and Diet Modifications
- Identifying and avoiding potential triggers such as heat, cold, or certain foods.
- Managing stress through relaxation techniques such as yoga and meditation.
- Using fragrance-free and hypoallergenic skincare products to prevent irritation.
Preventing Future Hives Outbreaks
Although chronic hives can be unpredictable, certain preventive measures can help reduce flare-ups:
- Keep a symptom diary – Track food, activities, stress levels, and potential triggers.
- Avoid known allergens – If allergy testing reveals specific triggers, make necessary lifestyle adjustments.
- Follow your prescribed treatment plan – Take medications as directed by your specialist to prevent recurrences.
- Manage stress levels – Stress and anxiety can exacerbate chronic hives, so practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques can help.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can chronic hives go away on their own?
In some cases, chronic hives resolve spontaneously, but they can persist for months or years. A specialist can help manage symptoms effectively.
2. Are chronic hives a sign of an autoimmune disease?
Yes, chronic hives are sometimes linked to autoimmune conditions like lupus or thyroid disorders. Blood tests can help determine if an autoimmune disease is a contributing factor.
3. Can stress cause chronic hives?
Stress does not directly cause hives but can trigger or worsen symptoms in some individuals. Managing stress may help reduce flare-ups.
4. What foods should I avoid if I have chronic hives?
While food triggers vary, common culprits include shellfish, nuts, dairy, and artificial preservatives. An elimination diet under a specialist’s guidance can help identify problem foods.
5. Can antihistamines cure chronic hives?
Antihistamines control symptoms but do not cure chronic hives. If hives persist despite antihistamine use, a specialist can recommend alternative treatments.
Conclusion
Chronic hives can be frustrating and disruptive, but with the help of hives specialists, individuals can find long-term relief. Specialists such as allergists, dermatologists, and immunologists can diagnose the root cause of chronic hives and provide targeted treatments, including antihistamines, biologic therapy, and immunosuppressants. By identifying triggers and following a personalized treatment plan, individuals can manage chronic hives effectively and improve their quality of life.