This article delves into the intricate workings of the 5G infrastructure market, exploring its current state, future projections, key drivers, and the impact it will have on various industries.
Understanding 5G Infrastructure
5G infrastructure encompasses the intricate network of technologies that facilitate the deployment and operation of 5G networks. It's a complex ecosystem consisting of three primary components:
- Radio Access Network (RAN): This critical layer connects user devices to the core network. It includes base stations, small cells, and massive MIMO (Multiple-Input and Multiple-Output) antennas, responsible for transmitting and receiving data signals.
- Core Network: The brain of the operation, the core network manages data routing, security, and user authentication. It utilizes advanced technologies like Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) for increased flexibility and scalability.
- Transport Network: The high-speed data highway, the transport network bridges the gap between the RAN and core network. It leverages fiber optics and microwave technologies to ensure seamless data transmission.
Market Size and Growth Trajectory
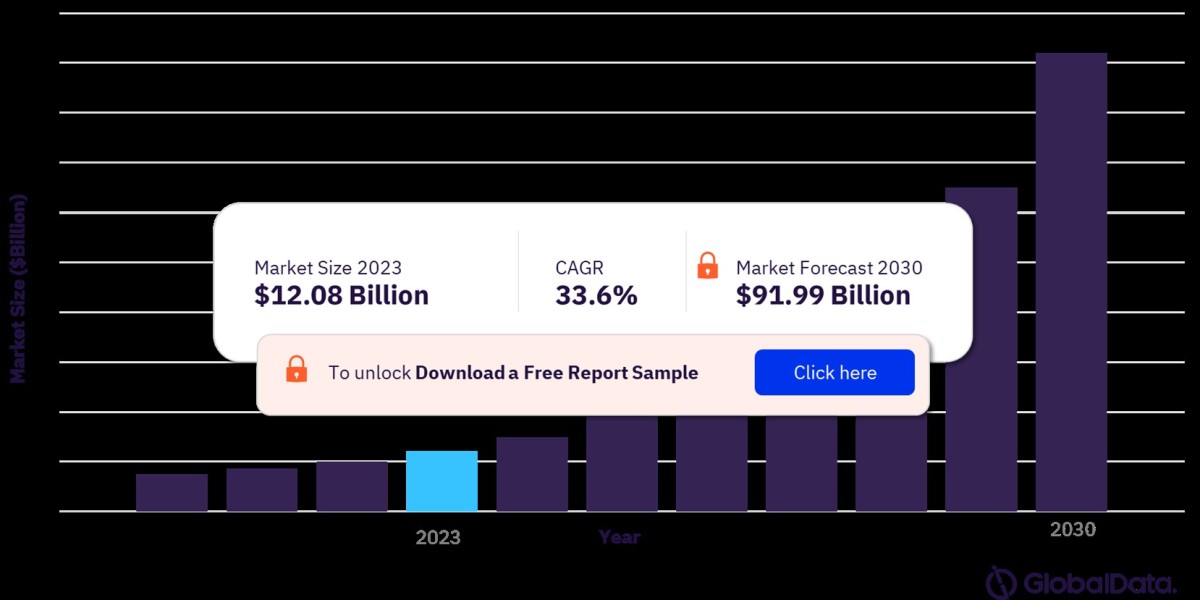
The 5G infrastructure market is experiencing phenomenal growth. While estimates vary slightly between research firms, the overall picture is one of remarkable expansion. Here's a glimpse into industry projections:
- MarketsandMarkets: Projects the market to reach a staggering USD 47.78 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 67.1%.
- Grand View Research: Estimates the market size at USD 16.69 billion in 2023 and anticipates a CAGR of 22.9% from 2024 to 2030.
- Mordor Intelligence: Places the market size at USD 9.87 billion in 2024 and forecasts a CAGR of 47.51% to reach USD 69.01 billion by 2029.
- Fortune Business Insights: Values the market at USD 25.69 billion in 2023 and predicts a phenomenal CAGR of 42.7% to reach a whopping USD 590.18 billion by 2032.
These figures paint a clear picture: the 5G infrastructure market is on a fast track to becoming a multi-billion dollar industry within the next decade.
Key Drivers of Market Growth
Several factors are propelling the 5G infrastructure market forward:
- Surging Mobile Data Traffic: With the proliferation of smartphones, tablets, and the Internet of Things (IoT), data consumption is skyrocketing. 5G's superior speed and capacity are crucial for handling this ever-increasing demand.
- Government Initiatives: Recognizing the transformative potential of 5G, governments worldwide are actively promoting its deployment through subsidies, spectrum allocation policies, and infrastructure development plans.
- Smart City and Industry 4.0 Applications: 5G's low latency and high reliability are perfect for real-time applications like smart grid management, autonomous vehicles, and remote surgery. This fosters investment in 5G infrastructure by various industries.
- Demand for Enhanced User Experience: Consumers are craving faster download speeds, seamless streaming, and superior connectivity. 5G infrastructure caters to this growing desire for a more robust mobile experience.
Market Segmentation and Trends
The 5G infrastructure market can be segmented based on various factors:
- Communication Infrastructure: This segment is further divided into small cells and macro cells. Small cells, with their ability to increase network capacity in dense urban areas, are expected to witness significant growth.
- Core Network: The trend leans towards Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) technologies for increased efficiency and flexibility.
- Network Architecture: Standalone (SA) 5G networks offer superior performance but require a complete overhaul of existing infrastructure. Non-standalone (NSA) 5G utilizes existing 4G infrastructure, making it a more readily deployable option in the initial stages.
- Operational Frequency: The market is divided into sub-6 GHz and mmWave (millimeter wave) frequencies. Sub-6 GHz offers wider coverage, while mmWave provides ultra-high speeds but with a shorter range.
- End User: The market caters to various end users, including telecom operators, enterprises, and government agencies. Each segment has its specific needs and growth patterns.
View Sample Report for Additional Insights on 5G Infrastructure Market Forecast, Download a Free Report Sample