Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is a painful condition that occurs after a shingles outbreak, causing persistent nerve pain. Managing this chronic pain can be challenging, but medications like Gabapentin 400 mg offer relief. Gabapentin, the active ingredient in the brand-name drug Neurontin, is commonly prescribed for PHN due to its ability to calm overactive nerve signals.
In this blog, we’ll explore how Gabapentin 400 mg works for postherpetic neuralgia, its effectiveness, dosage guidelines, potential side effects, and important precautions.
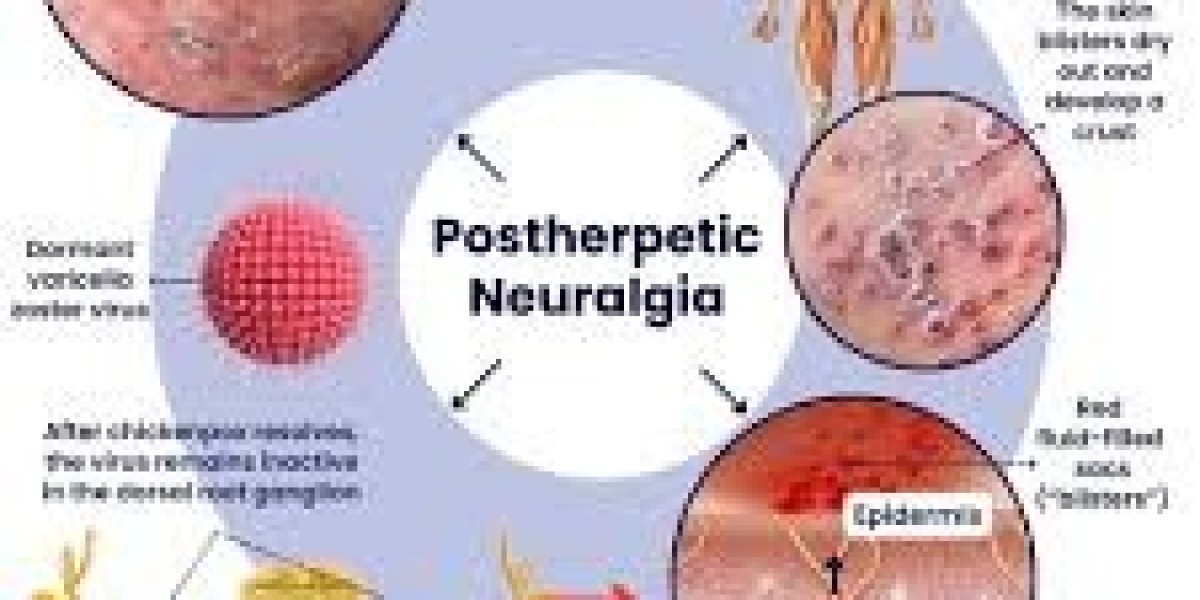
What is Postherpetic Neuralgia (PHN)?
Postherpetic neuralgia is a complication of shingles, caused by the varicella-zoster virus—the same virus responsible for chickenpox. After a shingles rash heals, some individuals continue to experience severe burning, stabbing, or throbbing pain in the affected area. This happens because the virus damages nerve fibers, sending incorrect pain signals to the brain.
PHN can last for months or even years, significantly impacting quality of life. Effective treatment is essential to manage symptoms, and Gabapentin 400 mg is one of the key medications used for this purpose.
How Does Gabapentin 400 mg Work for PHN?
Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin, is an anticonvulsant that also helps relieve nerve pain. While its exact mechanism isn’t fully understood, researchers believe it works by:
Modulating calcium channels in nerve cells reduces excessive electrical activity.
Decreasing the release of excitatory neurotransmitters that amplify pain signals.
Stabilizing hyperactive nerves that cause chronic pain in PHN.
Unlike traditional painkillers that target inflammation, Gabapentin specifically addresses neuropathic pain, making it a preferred choice for PHN.
Effectiveness of Gabapentin 400 mg for PHN
Clinical studies have demonstrated that Gabapentin is effective in reducing PHN pain. A typical starting dose is 300 mg per day, gradually increasing to 400 mg or higher based on patient response. Research shows that:
Gabapentin 400 mg significantly reduces pain intensity compared to a placebo.
Improves sleep and daily functioning by minimizing discomfort.
Works best when taken consistently, as its effects build up over time.
Patients often report noticeable pain relief within a few weeks of starting treatment. However, individual responses vary, and some may require dose adjustments.
Dosage Guidelines for Gabapentin 400 mg in PHN
Doctors usually prescribe Gabapentin in a step-wise approach to minimize side effects:
Initial Dose: 300 mg once daily (usually at bedtime).
Gradual Increase: After a few days, the dose may increase to 300 mg twice daily.
Maintenance Dose: If needed, the doctor may adjust to 400 mg or higher, up to a maximum of 3600 mg per day (divided into three doses).
Important Notes:
Never abruptly stop Gabapentin—tapering off is necessary to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
Take it at the same time daily for consistent pain control.
Higher doses don’t always mean better results—follow your doctor’s recommendations.
Potential Side Effects of Gabapentin 400 mg
While Gabapentin is generally well-tolerated, some users may experience side effects, including:
Common Side Effects:
Dizziness
Drowsiness
Fatigue
Mild nausea
Swelling in the extremities
Less Common but Serious Side Effects:
Mood changes (anxiety, depression)
Unsteady gait (increased fall risk in elderly patients)
Allergic reactions (rash, swelling, difficulty breathing)
If severe side effects occur, seek medical attention immediately.
Precautions & Interactions
Before taking Gabapentin 400 mg for PHN, consider the following:
Who Should Avoid Gabapentin?
People with kidney disease (dose adjustments may be needed).
Those with a history of drug allergies to Gabapentin or Neurontin.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women (only under strict medical supervision).
Drug Interactions:
Alcohol increases drowsiness and dizziness.
Antacids may reduce Gabapentin absorption (take 2 hours apart).
Opioids or sedatives can enhance CNS depression.
Always inform your doctor about all medications and supplements you’re taking.
Lifestyle Tips to Enhance Gabapentin’s Effectiveness
While Gabapentin helps manage PHN pain, combining it with lifestyle changes can improve outcomes:
Practice stress management (meditation, deep breathing).
Engage in gentle exercise (yoga, walking) to improve circulation.
Maintain a healthy diet (anti-inflammatory foods may help).
Follow a consistent sleep schedule to aid nerve recovery.
Conclusion
Gabapentin 400 mg (Neurontin) is a proven treatment for postherpetic neuralgia, offering relief by targeting nerve-related pain. While it may cause mild side effects, most patients tolerate it well when taken as prescribed. Always follow your doctor’s dosage instructions and report any unusual symptoms.